Page 339 - Read Online
P. 339
Page 10 of 14 Khan. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:45 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.58
A B
C D
E F
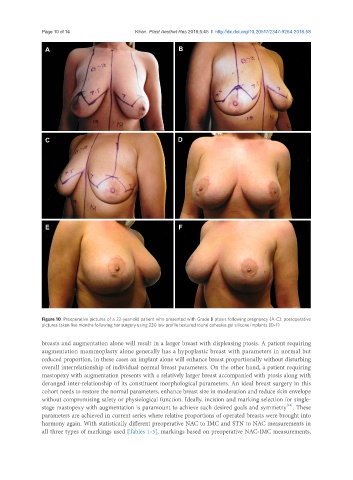
Figure 10. Preoperative pictures of a 22-year-old patient who presented with Grade B ptosis following pregnancy (A-C); postoperative
pictures taken five months following her surgery using 230 low profile textured round cohesive gel silicone implants (D-F)
breasts and augmentation alone will result in a larger breast with displeasing ptosis. A patient requiring
augmentation mammoplasty alone generally has a hypoplastic breast with parameters in normal but
reduced proportion, in these cases an implant alone will enhance breast proportionally without disturbing
overall interrelationship of individual normal breast parameters. On the other hand, a patient requiring
mastopexy with augmentation presents with a relatively larger breast accompanied with ptosis along with
deranged inter-relationship of its constituent morphological parameters. An ideal breast surgery in this
cohort needs to restore the normal parameters, enhance breast size in moderation and reduce skin envelope
without compromising safety or physiological function. Ideally, incision and marking selection for single-
[18]
stage mastopexy with augmentation is paramount to achieve such desired goals and symmetry . These
parameters are achieved in current series where relative proportions of operated breasts were brought into
harmony again. With statistically different preoperative NAC to IMC and STN to NAC measurements in
all three types of markings used [Tables 1-3], markings based on preoperative NAC-IMC measurements,