Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Page 4 of 9 Sforza et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:2 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2017.35
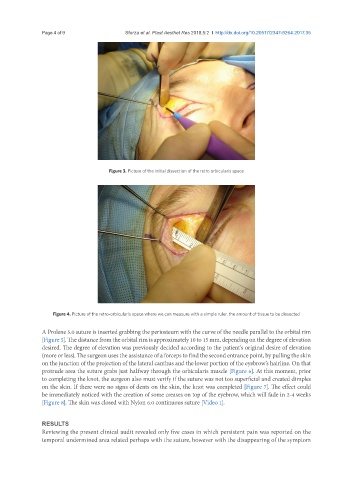
Figure 3. Picture of the initial dissection of the retro orbicularis space
Figure 4. Picture of the retro-orbicularis space where we can measure with a simple ruler, the amount of tissue to be dissected
A Prolene 5.0 suture is inserted grabbing the periosteum with the curve of the needle parallel to the orbital rim
[Figure 5]. The distance from the orbital rim is approximately 10 to 15 mm, depending on the degree of elevation
desired. The degree of elevation was previously decided according to the patient’s original desire of elevation
(more or less). The surgeon uses the assistance of a forceps to find the second entrance point, by pulling the skin
on the junction of the projection of the lateral canthus and the lower portion of the eyebrow’s hairline. On that
protrude area the suture grabs just halfway through the orbicularis muscle [Figure 6]. At this moment, prior
to completing the knot, the surgeon also must verify if the suture was not too superficial and created dimples
on the skin. If there were no signs of dents on the skin, the knot was completed [Figure 7]. The effect could
be immediately noticed with the creation of some creases on top of the eyebrow, which will fade in 2-4 weeks
[Figure 8]. The skin was closed with Nylon 6.0 continuous suture [Video 1].
RESULTS
Reviewing the present clinical audit revealed only five cases in which persistent pain was reported on the
temporal undermined area related perhaps with the suture, however with the disappearing of the symptom