Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
Sforza et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:2 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2017.35 Page 3 of 9
Reference point
Orbicularis
oculi muscle
Orbital septum
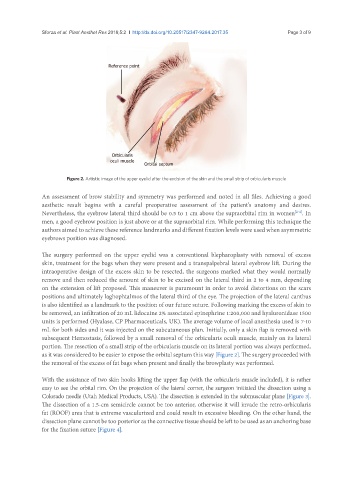
Figure 2. Artistic image of the upper eyelid after the excision of the skin and the small strip of orbicularis muscle
An assessment of brow stability and symmetry was performed and noted in all files. Achieving a good
aesthetic result begins with a careful preoperative assessment of the patient’s anatomy and desires.
Nevertheless, the eyebrow lateral third should be 0.5 to 1 cm above the supraorbital rim in women . In
[2-4]
men, a good eyebrow position is just above or at the supraorbital rim. While performing this technique the
authors aimed to achieve these reference landmarks and different fixation levels were used when asymmetric
eyebrows position was diagnosed.
The surgery performed on the upper eyelid was a conventional blepharoplasty with removal of excess
skin, treatment for the bags when they were present and a transpalpebral lateral eyebrow lift. During the
intraoperative design of the excess skin to be resected, the surgeons marked what they would normally
remove and then reduced the amount of skin to be excised on the lateral third in 2 to 4 mm, depending
on the extension of lift proposed. This maneuver is paramount in order to avoid distortions on the scars
positions and ultimately laghophtalmos of the lateral third of the eye. The projection of the lateral canthus
is also identified as a landmark to the position of our future suture. Following marking the excess of skin to
be removed, an infiltration of 20 mL lidocaine 2% associated epinephrine 1:200,000 and hyaluronidase 1500
units is performed (Hyalase, CP Pharmaceuticals, UK). The average volume of local anesthesia used is 7-10
mL for both sides and it was injected on the subcutaneous plan. Initially, only a skin flap is removed with
subsequent Hemostasis, followed by a small removal of the orbicularis oculi muscle, mainly on its lateral
portion. The resection of a small strip of the orbicularis muscle on its lateral portion was always performed,
as it was considered to be easier to expose the orbital septum this way [Figure 2]. The surgery proceeded with
the removal of the excess of fat bags when present and finally the browplasty was performed.
With the assistance of two skin hooks lifting the upper flap (with the orbicularis muscle included), it is rather
easy to see the orbital rim. On the projection of the lateral corner, the surgeon initiated the dissection using a
Colorado needle (Utah Medical Products, USA). The dissection is extended in the submuscular plane [Figure 3].
The dissection of a 1.5-cm semicircle cannot be too anterior, otherwise it will invade the retro-orbicularis
fat (ROOF) area that is extreme vascularized and could result in excessive bleeding. On the other hand, the
dissection plane cannot be too posterior as the connective tissue should be left to be used as an anchoring base
for the fixation suture [Figure 4].