Page 91 - Read Online
P. 91
Moreno-Sánchez et al. Double-paddled PMMF for complex orocervical defects
A
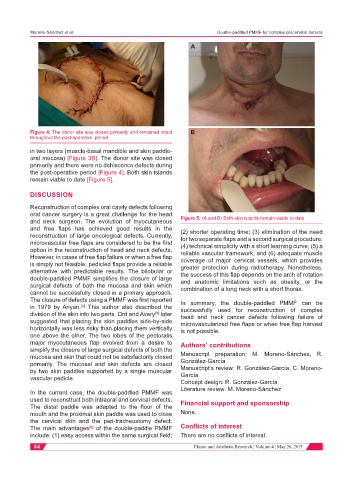
Figure 4: The donor site was closed primarily and remained intact B
throughout the post-operative period
in two layers (muscle-basal mandible and skin paddle-
oral mucosa) [Figure 3B]. The donor site was closed
primarily and there were no dehiscence defects during
the post-operative period [Figure 4]. Both skin islands
remain viable to date [Figure 5].
DISCUSSION
Reconstruction of complex oral cavity defects following
oral cancer surgery is a great challenge for the head
and neck surgeon. The evolution of myocutaneous Figure 5: (A and B) Both skin islands remain viable to date
and free flaps has achieved good results in the (2) shorter operating time; (3) elimination of the need
reconstruction of large oncological defects. Currently, for two separate flaps and a second surgical procedure;
microvascular free flaps are considered to be the first (4) technical simplicity with a short learning curve; (5) a
option in the reconstruction of head and neck defects. reliable vascular framework; and (6) adequate muscle
However, in cases of free flap failure or when a free flap coverage of major cervical vessels, which provides
is simply not feasible, pedicled flaps provide a reliable greater protection during radiotherapy. Nonetheless,
alternative with predictable results. The bilobular or the success of this flap depends on the arch of rotation
double-paddled PMMF simplifies the closure of large and anatomic limitations such as obesity, or the
surgical defects of both the mucosa and skin which combination of a long neck with a short thorax.
cannot be successfully closed in a primary approach.
The closure of defects using a PMMF was first reported In summary, the double-paddled PMMF can be
in 1979 by Ariyan. This author also described the successfully used for reconstruction of complex
[4]
division of the skin into two parts. Ord and Avery later head and neck cancer defects following failure of
[5]
suggested that placing the skin paddles side-by-side microvascularized free flaps or when free flap harvest
horizontally was less risky than placing them vertically is not possible.
one above the other. The two lobes of the pectoralis
major myocutaneous flap evolved from a desire to Authors’ contributions
simplify the closure of large surgical defects of both the
mucosa and skin that could not be satisfactorily closed Manuscript preparation: M. Moreno-Sánchez, R.
primarily. The mucosal and skin defects are closed González-García
by two skin paddles supported by a single muscular Manuscript’s review: R. González-García, C. Moreno-
vascular pedicle. García
Concept design: R. González-García
Literature review: M. Moreno-Sánchez
In the current case, the double-paddled PMMF was
used to reconstruct both intraoral and cervical defects. Financial support and sponsorship
The distal paddle was adapted to the floor of the
mouth and the proximal skin paddle was used to close None.
the cervical skin and the peri-tracheostomy defect.
The main advantages of the double-paddle PMMF Conflicts of interest
[6]
include: (1) easy access within the same surgical field; There are no conflicts of interest.
84 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ May 26, 2017