Page 241 - Read Online
P. 241
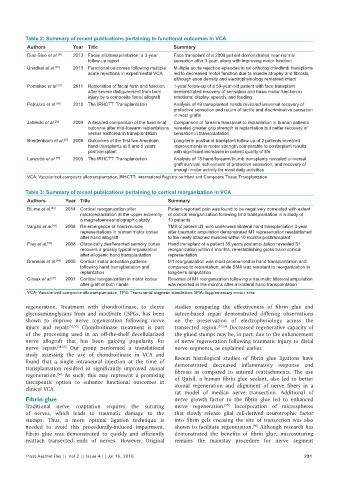
Table 2: Summary of recent publications pertaining to functional outcomes in VCA
Authors Year Title Summary
Diaz-Siso et al. [34] 2013 Facial allotransplantation: a 3-year Face transplant of a 2009 patient demonstrated near-normal
follow-up report sensation after 3-year, along with improving motor function
Unadkat et al. [46] 2013 Functional outcomes following multiple Multiple acute rejection episodes in rat orthotopichindlimb transplants
acute rejections in experimental VCA led to decreased motor function due to muscle atrophy and fibrosis,
although axon density and electrophysiology remained intact
Pomahac et al. [37] 2011 Restoration of facial form and function 1-year follow-up of a 59-year-old patient with face transplant
after severe disfigurement from burn demonstrated recovery of sensation and basic motor function in
injury by a composite facial allograft emotional display, speech, and feeding
Petruzzo et al. [36] 2010 The IRHCTT. Transplantation Analysis of 49 transplanted hands revealed universal recovery of
protective sensation and return of tactile and discriminative sensation
in most grafts
Jablecki et al. [38] 2009 A detailed comparison of the functional Comparison of forearm transplant to replantation in human patients
outcome after mid-forearm replantations revealed greater grip strength in replantation but better recovery of
versus midforearm transplantation sensation in transplantation
Breidenbach et al. [47] 2008 Outcomes of the first two American Long-term posthand transplant follow-up of 2 patients revealed
hand transplants at 8 and 6 years improvements in motor strength comparable to postreplant results
posttransplant with significant increases in patient quality of life
Lanzetta et al. [35] 2005 The IRHCTT. Transplantation Analysis of 18 hand/forearm/thumb transplants revealed universal
graft survival, achievment of protective sensation, and recovery of
enough motor activity for most daily activities
VCA: Vascularized composite allotransplantation, IRHCTT: International Registry on Hand and Composite Tissue Transplantation
Table 3: Summary of recent publications pertaining to cortical reorganization in VCA
Authors Year Title Summary
Blume et al. [45] 2014 Cortical reorganization after Patient-reported pain was found to be negatively correlated with extent
macroreplantation at the upper extremity: of cortical reorganization following limb transplantation in a study of
a magnetoencephalographic study 13 patients
Vargas et al. [42] 2008 Re-emergence of hand-muscle TMS of patient LB, who underwent bilateral hand transplantation 3-year
representations in human motor cortex after traumatic amputation demonstrated M1 representation reestablished
after hand allograft to the newly attached muscles within 10 months posttransplant
Frey et al. [43] 2008 Chronically deafferented sensory cortex Hand transplant of a patient 35 years postamputation revealed S1
recovers a grossly typical organization reorganization within 4 months, re-establishing gross hand cortical
after allogenic hand transplantation representation
Brenneis et al. [44] 2005 Cortical motor activation patterns M1 reorganization was most pronounced in hand transplantation and
following hand transplantation and compared to replantation, while SMA was resistant to reorganization in
replantation long-term amputation
Giraux et al. [41] 2001 Cortical reorganization in motor cortex Reversal of M1 reorganization following a traumatic bilateral amputation
after graft of both hands was reported in the months after a bilateral hand transplantation
VCA: Vascularized composite allotransplantation, TMS: Transcranial magnetic stimulation, SMA: Supplementary motor area
regeneration. Treatment with chondroitinase, to cleave studies comparing the effectiveness of fibrin glue and
glycosaminoglycans from and inactivate CSPGs, has been suture‑based repair demonstrated differing observations
shown to improve nerve regeneration following nerve on the preservation of electrophysiology across the
injury and repair. [52,53] Chondroitinase treatment is part transected region. [57,58] Decreased regenerative capacity of
of the processing used in an off‑the‑shelf decellularized the glued stumps may be, in part, due to the enhancement
nerve allograft that has been gaining popularity for of nerve regeneration following traumatic injury to distal
nerve repair. [54,55] Our group performed a translational nerve segments, as explained earlier.
study assessing the use of chondroitinase in VCA and Recent histological studies of fibrin glue ligations have
found that a single intraneural injection at the time of demonstrated decreased inflammatory response and
transplantation resulted in significantly improved axonal fibrosis as compared to sutured reattachments. The use
regeneration. As such, this may represent a promising of Quixil, a human fibrin glue sealant, also led to better
[56]
therapeutic option to enhance functional outcomes in axonal regeneration and alignment of nerve fibers in a
clinical VCA.
rat model of median nerve transection. Additional of
Fibrin glue nerve growth factor to the fibrin glue led to enhanced
Traditional nerve coaptation requires the suturing nerve regeneration. Incorporation of microspheres
[59]
of nerves, which leads to traumatic damage to the that slowly release glial cell‑derived neurotrophic factor
stumps. Thus, a more optimal ligation technique is into fibrin gels encasing the site of transection was also
needed to avoid this procedurally‑induced impairment. shown to facilitate regeneration. Although research has
[60]
Fibrin glue was demonstrated to quickly and efficiently demonstrated the benefits of fibrin glue, microsuturing
reattach transected ends of nerves. However, Original remains the mainstay procedure for nerve segment
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 4 || Jul 15, 2015 231