Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
Flap design day later. The stitches were removed from the skin 5-7
Based on the designs of Zitelli and Baker, Xue et al. days later [Figures 1 and 2].
[1]
[2]
planned a superiorly based bilobed flap obtained from the
nasolabial region. First, two arcs were marked to define RESULTS
the boundaries of the flap and its proper angulations. The
radius and diameter of the nasal defect were measured Reconstruction procedures using the modified bilobed
with calipers. A pivot point was placed in the nasal flaps were performed in 34 cases with tissue defects of
sidewall and was located one radius from the free edge of the nasal tip. The study sample included 5 male and 29
the defect. The center line of the defect was marked. The female patients, with an average age of 27.14 ± 7.79
radius of the center arc was equal to the diameter of the years. Twenty patients presented with nevus, 8 with
nasal defect. The radius of the distal arc was equal to the granuloma, and 6 with fibroma. The size of the defects
distance between the distal edge of the defect and the ranged from 0.8 cm × 0.9 cm to 1.2 cm × 1.8 cm. All
pivot point. Based on the pivot point, the two arcs were defects were closed successfully without difficulty using
marked with a standard geometry compass. this technique. The defects were repaired under minimal
closure tension as a single-stage procedure. The patients
Second, the two lobes of the flap were configured. The were then followed for 3 months and 18 months. No
primary lobe was located between the defect and the severe complications were found to have occurred
cheek and was slightly larger than the primary defect. after any of the operations. There were no dissymmetry
The width of the primary lobe was equal to that of the deformities or retraction deformities of the nasal ala in
primary defect. The length of the primary lobe was 10% any of the cases.
longer than the distance of the distal defect edge to the
pivot point of the flap. The second lobe was located in We did not find any patient with nasal valve collapse,
the cheek and was slightly smaller than the primary lobe.
The length of the second lobe was 30% longer than the
distance of the distal defect edge to the pivot point of
the flap. The width of the second lobe was 90-100% of
that of the primary lobe. The two flaps rotated a total of
90°-100°. Based on the two arcs, the two lobes of the flap
were marked.
Surgical technique
The lesions were removed below the nasal superficial
musculoaponeurotic system. The specimens were sent
for histopathological examination to ensure clearance of
the margins.
Incisions were made along the previously described
markings. The primary lobe was undermined above the
perichondrium of the nasal cartilage to promote adequate
tissue perfusion of the flap. Once this layer was reached,
the flap was easily elevated. The second lobe was elevated
in the plane of the superficial fascia, and the pedicle
portion was separated with blunt dissection to preserve
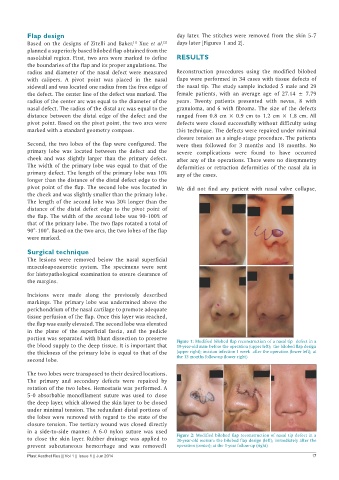
the blood supply to the deep tissue. It is important that Figure 1: Modified bilobed flap reconstruction of a nasal tip defect in a
19-year-old man: before the operation (upper left); the bilobed flap design
the thickness of the primary lobe is equal to that of the (upper right); incision infection 1 week after the operation (lower left); at
second lobe. the 13 months follow-up (lower right)
The two lobes were transposed to their desired locations.
The primary and secondary defects were repaired by
rotation of the two lobes. Hemostasis was performed. A
5-0 absorbable monofilament suture was used to close
the deep layer, which allowed the skin layer to be closed
under minimal tension. The redundant distal portions of
the lobes were removed with regard to the state of the
closure tension. The tertiary wound was closed directly
in a side-to-side manner. A 6-0 nylon suture was used
to close the skin layer. Rubber drainage was applied to Figure 2: Modified bilobed flap reconstruction of nasal tip defect in a
20-year-old woman: the bilobed flap design (left); immediately after the
prevent subcutaneous hemorrhage and was removed1 operation (center); at the 1-year follow-up (right)
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 1 || Jun 2014 17