Page 75 - Read Online
P. 75
Page 4 of 12 Mitchell et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:35 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2023.14
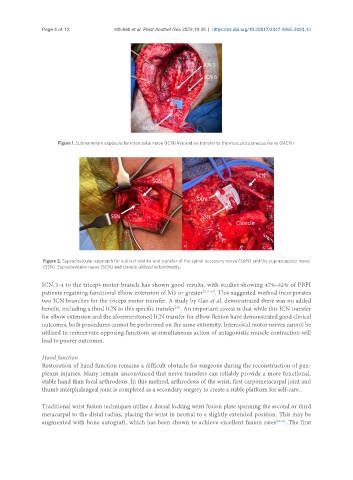
Figure 1. Submammary exposure for intercostal nerve (ICN) five and six transfer to the musculocutaneous nerve (MCN).
Figure 2. Supraclavicular approach for a direct end-to-end transfer of the spinal accessory nerve (SAN) and the suprascapular nerve
(SSN). Supraclavicular nerve (SCN) and clavicle utilized as landmarks.
ICN 3-4 to the triceps motor branch has shown good results, with studies showing 47%-82% of PBPI
patients regaining functional elbow extension of M3 or greater [9,19-21] . This suggested method incorporates
two ICN branches for the triceps motor transfer. A study by Gao et al. demonstrated there was no added
[21]
benefit, including a third ICN to this specific transfer . An important caveat is that while this ICN transfer
for elbow extension and the aforementioned ICN transfer for elbow flexion have demonstrated good clinical
outcomes, both procedures cannot be performed on the same extremity. Intercostal motor nerves cannot be
utilized to reinnervate opposing functions as simultaneous action of antagonistic muscle contraction will
lead to poorer outcomes.
Hand function
Restoration of hand function remains a difficult obstacle for surgeons during the reconstruction of pan-
plexus injuries. Many remain unconvinced that nerve transfers can reliably provide a more functional,
stable hand than focal arthrodesis. In this method, arthrodesis of the wrist, first carpometacarpal joint and
thumb interphalangeal joint is completed as a secondary surgery to create a stable platform for self-care.
Traditional wrist fusion techniques utilize a dorsal locking wrist fusion plate spanning the second or third
metacarpal to the distal radius, placing the wrist in neutral to a slightly extended position. This may be
augmented with bone autograft, which has been shown to achieve excellent fusion rates [22,23] . The first