Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
Page 10 of 17 Buncke. Plast Aesthet Res 2022;9:38 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.08
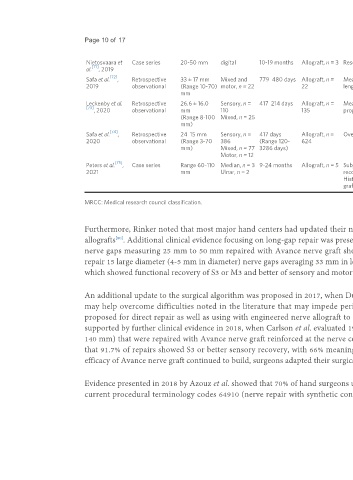
Nietosvaara et Case series 20-50 mm digital 10-19 months Allograft, n = 3 Resorption of the engineered nerve graft or neuroma proximal to the nerve graft
[71]
al. , 2019
[72]
Safa et al. , Retrospective 33 ± 17 mm Mixed and 779 480 days Allograft, n = Meaningful recovery was reported in 73% of repairs. No significant differences were noted between gap
2019 observational (Range 10-70) motor, n = 22 22 lengths or mechanism of injury
mm
Leckenby et al. Retrospective 26.6 ± 16.0 Sensory, n = 417 214 days Allograft, n = Meaningful recovery for motor (≥ M3) function in 36% of repairs and sensory (≥ S3) in 77% of repairs. Inferior
[73]
, 2020 observational mm 110 135 prognosis for larger diameter and longer grafts
(Range 8-100 Mixed, n = 25
mm)
[74]
Safa et al. , Retrospective 24 15 mm Sensory, n = 417 days Allograft, n = Overall meaningful recovery in 82% of repairs in sensory, mixed and motor nerve repairs
2020 observational (Range 3-70 386 (Range 120- 624
mm) Mixed, n = 77 3286 days)
Motor, n = 12
[75]
Peters et al. , Case series Range 60-110 Median, n = 3 9-24 months Allograft, n = 5 Subjects had previously experienced an iatrogenic injury. Subjects showed no clinical sensory or motor
2021 mm Ulnar, n = 2 recovery and showed significant neuropathic pain ranging between 8 and 10 on a 10-score visual analog scale.
Histology showed axonal regeneration stalling mid-graft in 3 of 5 grafts and no axonal regeneration in 2 of 5
grafts
MRCC: Medical research council classification.
Furthermore, Rinker noted that most major hand centers had updated their nerve repair algorithm as a result of the introduction of these engineered nerve
[80]
allografts . Additional clinical evidence focusing on long-gap repair was presented by Rinker et al. in 2017, where a patient population of 50 digital (sensory)
nerve gaps measuring 25 mm to 50 mm repaired with Avance nerve graft showed S3 or greater recovery in 86% of repairs . Use of Avance nerve graft to
[68]
repair 15 large diameter (4-5 mm in diameter) nerve gaps averaging 33 mm in length (range 5-50 mm) using a single Avance nerve graft was evaluated in 2017,
[67]
which showed functional recovery of S3 or M3 and better of sensory and motor function in 67% and 85% of repairs .
An additional update to the surgical algorithm was proposed in 2017, when Ducic et al. suggested that utilizing a nerve conduit for connector-assisted repair
may help overcome difficulties noted in the literature that may impede peripheral nerve regeneration after repair . This connector-assisted repair was
[81]
[81]
proposed for direct repair as well as using with engineered nerve allograft to prevent misalignment of the fascicles during the repair . This algorithm was
supported by further clinical evidence in 2018, when Carlson et al. evaluated 19 sensory, mixed, and motor nerve gaps averaging 65 mm in length (range, 10-
140 mm) that were repaired with Avance nerve graft reinforced at the nerve coaptation site with Axoguard nerve protector . Carlson and colleagues found
[70]
®
that 91.7% of repairs showed S3 or better sensory recovery, with 66% meaningful recovery in gap lengths greater than 50 mm . As clinical evidence of the
[70]
efficacy of Avance nerve graft continued to build, surgeons adapted their surgical algorithm to include the use of Avance nerve graft.
Evidence presented in 2018 by Azouz et al. showed that 70% of hand surgeons used engineered nerve allografts in their surgical practice, as noted by the use of
current procedural terminology codes 64910 (nerve repair with synthetic conduit or vein allograft), 64890 (nerve graft, single strand, hand, < 4 cm), 64831