Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
[44]
veins [Figure 5]. Almost all anastomoses were performed
using conventional end-to-end or end-to-side microsurgical
techniques.
Regarding facial nerve neurorrhaphy, some teams have
accessed to nerve via parotidectomy, performing the nerve
connection at recipient main trunk also including the parotid
glands in the allograft. Other teams have performed the
[21]
anastomosis at peripheral facial nerve branches doing an
intra-parotid nerve dissection [45,46] connecting only distal
branches to the parotid gland. [1,47] Regarding sensory nerves,
most teams connected infraorbital and mental nerves [48-51]
while the supraorbital nerve neurorrhaphy is preferably
Figure 4: Experimental model of a full face transplant in cadaver. (a) [35,36,52,53]
External and (b) internal view of the allograft carried out in full FT.
PRE-TRANSPLANT CONSIDERATIONS
In all cases a brain death donor is required besides the
consent of the family. Donors and recipients are matched on
the basis of race, sex, blood type, human leukocyte antigen
and skin color. [54,55] A full psychological evaluation before
including the recipient as a candidate on a FT program is
[56]
essential. Evident contraindications are psychological
disorders that impair the ability of the recipient to follow
the immunosuppressive protocol. Informed consent prior
to the FT requires a clear understanding of the risks of
surgery, immunosuppressive therapy and potential allograft
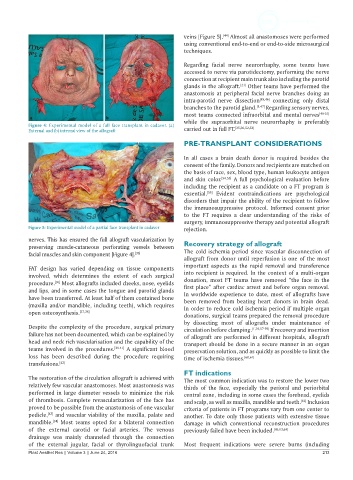
Figure 5: Experimental model of a partial face transplant in cadaver rejection.
nerves. This has ensured the full allograft vascularization by
preserving muscle-cutaneous perforating vessels between Recovery strategy of allograft
facial muscles and skin component [Figure 4]. [35] The cold ischemia period since vascular disconnection of
allograft from donor until reperfusion is one of the most
important aspects as the rapid removal and transference
FAT design has varied depending on tissue components
involved, which determines the extent of each surgical into recipient is required. In the context of a multi-organ
donation, most FT teams have removed “the face in the
procedure. Most allografts included cheeks, nose, eyelids first place” after cardiac arrest and before organ removal.
[36]
and lips, and in some cases the tongue and parotid glands In worldwide experience to date, most of allografts have
have been transferred. At least half of them contained bone been removed from beating heart donors in brain dead.
(maxilla and/or mandible, including teeth), which requires In order to reduce cold ischemia period if multiple organ
open osteosynthesis. [37,38] donations, surgical teams prepared the removal procedure
by dissecting most of allografts under maintenance of
Despite the complexity of the procedure, surgical primary circulation before clamping. [1,39,57-59] If recovery and insertion
failure has not been documented, which can be explained by of allograft are performed in different hospitals, allograft
head and neck rich vascularisation and the capability of the transport should be done in a secure manner in an organ
teams involved in the procedures. [39-41] A significant blood preservation solution, and as quickly as possible to limit the
loss has been described during the procedure requiring time of ischemia tissues. [60,61]
transfusions. [42]
FT indications
The restoration of the circulation allograft is achieved with The most common indication was to restore the lower two
relatively few vascular anastomoses. Most anastomosis was thirds of the face, especially the perioral and periorbital
performed in large diameter vessels to minimize the risk central zone, including in some cases the forehead, eyelids
of thrombosis. Complete revascularization of the face has and scalp, as well as maxilla, mandible and teeth. Inclusion
[62]
proved to be possible from the anastomosis of one vascular criteria of patients in FT programs vary from one center to
pedicle, and vascular viability of the maxilla, palate and another. To date only those patients with extensive tissue
[43]
[34]
mandible. Most teams opted for a bilateral connection damage in which conventional reconstruction procedures
of the external carotid or facial arteries. The venous previously failed have been included. [49,63,64]
drainage was mainly channeled through the connection
of the external jugular, facial or thyrolinguofacial trunk Most frequent indications were severe burns (including
Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || June 24, 2016 213