Page 76 - Read Online
P. 76
Page 4 of 11 El-Ghoneimi et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2022;9:39 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.101
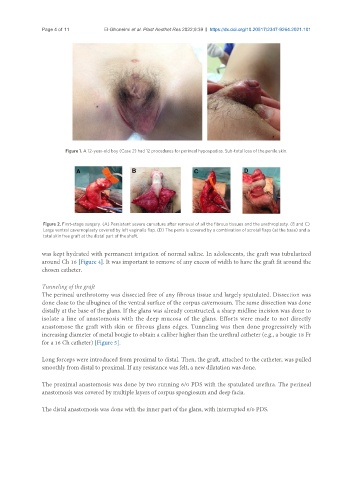
Figure 1. A 12-year-old boy (Case 2) had 12 procedures for perineal hypospadias. Sub-total loss of the penile skin.
Figure 2. First-stage surgery. (A) Persistent severe curvature after removal of all the fibrous tissues and the urethroplasty. (B and C)
Large ventral cavernoplasty covered by left vaginalis flap. (D) The penis is covered by a combination of scrotal flaps (at the base) and a
total skin free graft at the distal part of the shaft.
was kept hydrated with permanent irrigation of normal saline. In adolescents, the graft was tubularized
around Ch 16 [Figure 4]. It was important to remove of any excess of width to have the graft fit around the
chosen catheter.
Tunneling of the graft
The perineal urethrotomy was dissected free of any fibrous tissue and largely spatulated. Dissection was
done close to the albuginea of the ventral surface of the corpus cavernosum. The same dissection was done
distally at the base of the glans. If the glans was already constructed, a sharp midline incision was done to
isolate a line of anastomosis with the deep mucosa of the glans. Efforts were made to not directly
anastomose the graft with skin or fibrous glans edges. Tunneling was then done progressively with
increasing diameter of metal bougie to obtain a caliber higher than the urethral catheter (e.g., a bougie 18 Fr
for a 16 Ch catheter) [Figure 5].
Long forceps were introduced from proximal to distal. Then, the graft, attached to the catheter, was pulled
smoothly from distal to proximal. If any resistance was felt, a new dilatation was done.
The proximal anastomosis was done by two running 6/0 PDS with the spatulated urethra. The perineal
anastomosis was covered by multiple layers of corpus spongiosum and deep facia.
The distal anastomosis was done with the inner part of the glans, with interrupted 6/0 PDS.