Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Page 6 of 14 Brawley et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2022;9:6 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.107
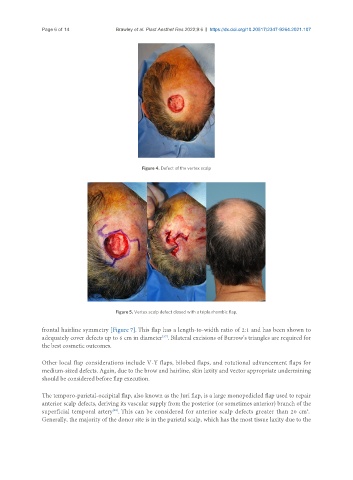
Figure 4. Defect of the vertex scalp
Figure 5. Vertex scalp defect closed with a triple rhombic flap.
frontal hairline symmetry [Figure 7]. This flap has a length-to-width ratio of 2:1 and has been shown to
adequately cover defects up to 6 cm in diameter . Bilateral excisions of Burrow’s triangles are required for
[37]
the best cosmetic outcomes.
Other local flap considerations include V-Y flaps, bilobed flaps, and rotational advancement flaps for
medium-sized defects. Again, due to the brow and hairline, skin laxity and vector appropriate undermining
should be considered before flap execution.
The temporo-parietal-occipital flap, also known as the Juri flap, is a large monopedicled flap used to repair
anterior scalp defects, deriving its vascular supply from the posterior (or sometimes anterior) branch of the
2
[38]
superficial temporal artery . This can be considered for anterior scalp defects greater than 20 cm .
Generally, the majority of the donor site is in the parietal scalp, which has the most tissue laxity due to the