Page 115 - Read Online
P. 115
Page 4 of 10 Mayland et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2021;8:62 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.38
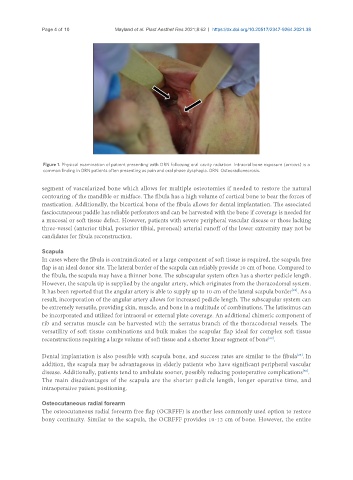
Figure 1. Physical examination of patient presenting with ORN following oral cavity radiation. Intraoral bone exposure (arrows) is a
common finding in ORN patients often presenting as pain and oral phase dysphagia. ORN: Osteoradionecrosis.
segment of vascularized bone which allows for multiple osteotomies if needed to restore the natural
contouring of the mandible or midface. The fibula has a high volume of cortical bone to bear the forces of
mastication. Additionally, the bicortical bone of the fibula allows for dental implantation. The associated
fasciocutaneous paddle has reliable perforators and can be harvested with the bone if coverage is needed for
a mucosal or soft tissue defect. However, patients with severe peripheral vascular disease or those lacking
three-vessel (anterior tibial, posterior tibial, peroneal) arterial runoff of the lower extremity may not be
candidates for fibula reconstruction.
Scapula
In cases where the fibula is contraindicated or a large component of soft tissue is required, the scapula free
flap is an ideal donor site. The lateral border of the scapula can reliably provide 10 cm of bone. Compared to
the fibula, the scapula may have a thinner bone. The subscapular system often has a shorter pedicle length.
However, the scapula tip is supplied by the angular artery, which originates from the thoracodorsal system.
[28]
It has been reported that the angular artery is able to supply up to 10 cm of the lateral scapula border . As a
result, incorporation of the angular artery allows for increased pedicle length. The subscapular system can
be extremely versatile, providing skin, muscle, and bone in a multitude of combinations. The latissimus can
be incorporated and utilized for intraoral or external plate coverage. An additional chimeric component of
rib and serratus muscle can be harvested with the serratus branch of the thoracodorsal vessels. The
versatility of soft tissue combinations and bulk makes the scapular flap ideal for complex soft tissue
[29]
reconstructions requiring a large volume of soft tissue and a shorter linear segment of bone .
[28]
Dental implantation is also possible with scapula bone, and success rates are similar to the fibula . In
addition, the scapula may be advantageous in elderly patients who have significant peripheral vascular
disease. Additionally, patients tend to ambulate sooner, possibly reducing postoperative complications .
[30]
The main disadvantages of the scapula are the shorter pedicle length, longer operative time, and
intraoperative patient positioning.
Osteocutaneous radial forearm
The osteocutaneous radial forearm free flap (OCRFFF) is another less commonly used option to restore
bony continuity. Similar to the scapula, the OCRFFF provides 10-12 cm of bone. However, the entire