Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
Gossett et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2021;8:60 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.69 Page 11 of 14
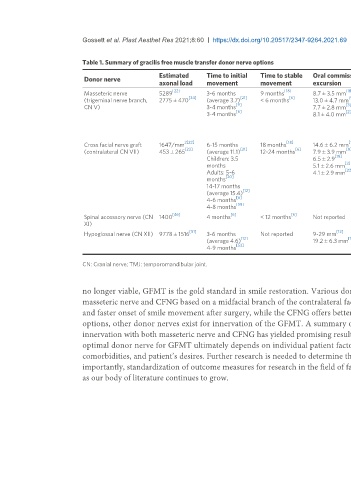
Table 1. Summary of gracilis free muscle transfer donor nerve options
Estimated Time to initial Time to stable Oral commissure
Donor nerve Spontaneity Stages Morbidity
axonal load movement movement excursion
[22] [18] [18] [21]
Masseteric nerve 5289 3-6 months 9 months 8.7 ± 3.5 mm 0% One Masseter muscle atrophy without dysarthria; rare TMJ
[24] [21] [6] [9] [14]
(trigeminal nerve branch, 2775 ± 470 (average 3.7) < 6 months 13.0 ± 4.7 mm 20% dysfunction; prandial facial movement rarely considered
[9] [3] [13]
CN V) 3-4 months 7.7 ± 2.8 mm 0% bothersome
[6] [22] [19]
3-4 months 8.1 ± 4.0 mm 55.5%
Women:
70.6%
[19]
Men: 42.1%
2[22] [18] [12] [21]
Cross facial nerve graft 1647/mm 6-15 months 18 months 14.6 ± 6.2 mm 34% Typically two, can be Sensory disturbance with sural nerve harvest
[23] [21] [6] [8] [14]
(contralateral CN VII) 453 ± 265 (average 11.1) 12-24 months 7.9 ± 3.9 mm 75% done as a single stage
[18] [13]
Children: 3.5 6.5 ± 2.9 100%
[3]
months 5.1 ± 2.6 mm
Adults: 5-6 4.1 ± 2.9 mm [22]
[20]
months
14-17 months
[12]
(average 15.4)
[6]
4-6 months
[58]
4-8 months
[46] [6] [6] [6]
Spinal accessory nerve (CN 1400 4 months < 12 months Not reported 45% One Ipsilateral trapezius weakness and shoulder pain
XI)
[51] [12]
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) 9778 ± 1516 3-6 months Not reported 9-29 mm None reported One Hemitongue atrophy, speech and swallowing dysfunction
[12] [12]
(average 4.6) 19.2 ± 6.3 mm
[53]
4-9 months
CN: Cranial nerve; TMJ: temporomandibular joint.
no longer viable, GFMT is the gold standard in smile restoration. Various donor nerve options exist for innervating GFMT, most commonly the ipsilateral
masseteric nerve and CFNG based on a midfacial branch of the contralateral facial nerve. In general, masseteric nerve innervation provides superior excursion
and faster onset of smile movement after surgery, while the CFNG offers better spontaneity of smile. In patients for whom masseteric nerve or CFNG are not
options, other donor nerves exist for innervation of the GFMT. A summary of the various donor nerves discussed in this review is shown in Table 1. Dual
innervation with both masseteric nerve and CFNG has yielded promising results in GFMT, taking advantage of the benefits of each donor source. Selecting an
optimal donor nerve for GFMT ultimately depends on individual patient factors, including etiology of the facial paralysis, availability of donor options, age,
comorbidities, and patient’s desires. Further research is needed to determine the optimal staging and pattern of coaptation for dually innervated GFMT. Most
importantly, standardization of outcome measures for research in the field of facial paralysis will be crucial to effectively compare and reproduce future results
as our body of literature continues to grow.