Page 77 - Read Online
P. 77
Page 8 of 11 Matiasek et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:36 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.50
6.0
5.0
4.0 3.19 3.79
Log reduction 3.0 2.16 2.58 saline solution
®
octenilin Wound Irrigation Solution
®
Serasept 2
< 1.95
< 1.95
2.0
Prontosan ®
1.0
0.0
0.5 2
Time [min]
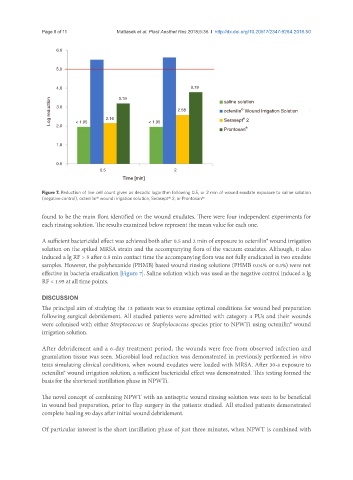
Figure 7. Reduction of live cell count given as decadic logarithm following 0.5, or 2 min of wound exudate exposure to saline solution
(negative control), octenilin® wound irrigation solution, Serasept® 2, or Prontosan®
found to be the main flora identified on the wound exudates. There were four independent experiments for
each rinsing solution. The results examined below represent the mean value for each one.
A sufficient bactericidal effect was achieved both after 0.5 and 2 min of exposure to octenilin® wound irrigation
solution on the spiked MRSA strain and the accompanying flora of the vacuum exudates. Although, it also
induced a lg RF > 5 after 0.5 min contact time the accompanying flora was not fully eradicated in two exudate
samples. However, the polyhexanide (PHMB) based wound rinsing solutions (PHMB 0.04% or 0.1%) were not
effective in bacteria eradication [Figure 7]. Saline solution which was used as the negative control induced a lg
RF < 1.95 at all time points.
DISCUSSION
The principal aim of studying the 13 patients was to examine optimal conditions for wound bed preparation
following surgical debridement. All studied patients were admitted with category 4 PUs and their wounds
were colonised with either Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species prior to NPWTi using octenilin® wound
irrigation solution.
After debridement and a 6-day treatment period, the wounds were free from observed infection and
granulation tissue was seen. Microbial load reduction was demonstrated in previously performed in vitro
tests simulating clinical conditions, when wound exudates were loaded with MRSA. After 30-s exposure to
octenilin® wound irrigation solution, a sufficient bactericidal effect was demonstrated. This testing formed the
basis for the shortened instillation phase in NPWTi.
The novel concept of combining NPWT with an antiseptic wound rinsing solution was seen to be beneficial
in wound bed preparation, prior to flap surgery in the patients studied. All studied patients demonstrated
complete healing 90 days after initial wound debridement.
Of particular interest is the short instillation phase of just three minutes, when NPWT is combined with