Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Fisher et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2024;11:36 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2024.53 Page 3 of 13
Figure 1. Preoperative MRA of lumbar perforator vessels. MRA: Magnetic resonance angiogram; ES: erector spinae; QL: quadratus
lumborum.
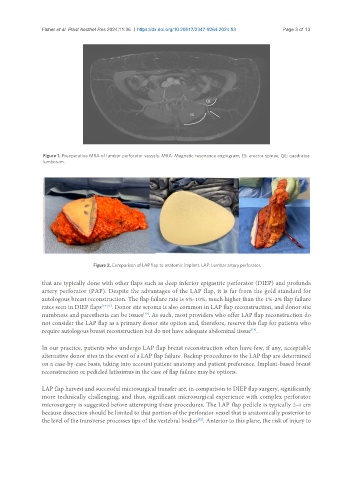
Figure 2. Comparison of LAP flap to anatomic implant. LAP: Lumbar artery perforator.
that are typically done with other flaps such as deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) and profunda
artery perforator (PAP). Despite the advantages of the LAP flap, it is far from the gold standard for
autologous breast reconstruction. The flap failure rate is 6%-10%, much higher than the 1%-2% flap failure
rates seen in DIEP flaps [19-21] . Donor site seroma is also common in LAP flap reconstruction, and donor site
[19]
numbness and paresthesia can be issues . As such, most providers who offer LAP flap reconstruction do
not consider the LAP flap as a primary donor site option and, therefore, reserve this flap for patients who
[18]
require autologous breast reconstruction but do not have adequate abdominal tissue .
In our practice, patients who undergo LAP flap breast reconstruction often have few, if any, acceptable
alternative donor sites in the event of a LAP flap failure. Backup procedures to the LAP flap are determined
on a case-by-case basis, taking into account patient anatomy and patient preference. Implant-based breast
reconstruction or pedicled latissimus in the case of flap failure may be options.
LAP flap harvest and successful microsurgical transfer are, in comparison to DIEP flap surgery, significantly
more technically challenging, and thus, significant microsurgical experience with complex perforator
microsurgery is suggested before attempting these procedures. The LAP flap pedicle is typically 2-4 cm
because dissection should be limited to that portion of the perforator vessel that is anatomically posterior to
the level of the transverse processes tips of the vertebral bodies . Anterior to this plane, the risk of injury to
[22]