Page 60 - Read Online
P. 60
Park et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.98 Page 3 of 10
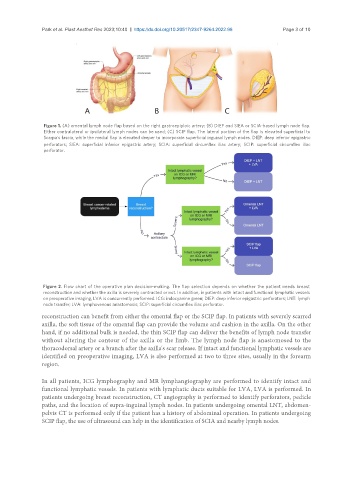
Figure 1. (A) omental lymph node flap based on the right gastroepiploic artery; (B) DIEP and SIEA or SCIA-based lymph node flap.
Either contralateral or ipsilateral lymph nodes can be used; (C) SCIP flap. The lateral portion of the flap is elevated superficial to
Scarpa's fascia, while the medial flap is elevated deeper to incorporate superficial inguinal lymph nodes. DIEP: deep inferior epigastric
perforators; SIEA: superficial inferior epigastric artery; SCIA: superficial circumflex iliac artery; SCIP: superficial circumflex iliac
perforator.
Figure 2. Flow chart of the operative plan decision-making. The flap selection depends on whether the patient needs breast
reconstruction and whether the axilla is severely contracted or not. In addition, in patients with intact and functional lymphatic vessels
on preoperative imaging, LVA is concurrently performed. ICG: indocyanine green; DIEP: deep inferior epigastric perforators; LNT: lymph
node transfer; LVA: lymphovenous anastomosis; SCIP: superficial circumflex iliac perforator.
reconstruction can benefit from either the omental flap or the SCIP flap. In patients with severely scarred
axilla, the soft tissue of the omental flap can provide the volume and cushion in the axilla. On the other
hand, if no additional bulk is needed, the thin SCIP flap can deliver the benefits of lymph node transfer
without altering the contour of the axilla or the limb. The lymph node flap is anastomosed to the
thoracodorsal artery or a branch after the axilla's scar release. If intact and functional lymphatic vessels are
identified on preoperative imaging, LVA is also performed at two to three sites, usually in the forearm
region.
In all patients, ICG lymphography and MR lymphangiography are performed to identify intact and
functional lymphatic vessels. In patients with lymphatic ducts suitable for LVA, LVA is performed. In
patients undergoing breast reconstruction, CT angiography is performed to identify perforators, pedicle
paths, and the location of supra-inguinal lymph nodes. In patients undergoing omental LNT, abdomen-
pelvis CT is performed only if the patient has a history of abdominal operation. In patients undergoing
SCIP flap, the use of ultrasound can help in the identification of SCIA and nearby lymph nodes.