Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
Chen et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:5 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.117 Page 3 of 5
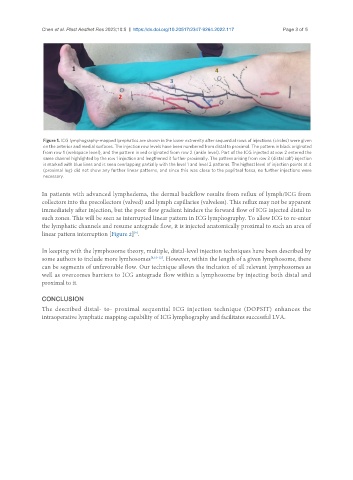
Figure 1. ICG lymphography-mapped lymphatics are shown in the lower extremity after sequential rows of injections (circles) were given
on the anterior and medial surfaces. The injection row levels have been numbered from distal to proximal. The pattern in black originated
from row 1 (webspace level), and the pattern in red originated from row 2 (ankle level). Part of the ICG injected at row 2 entered the
same channel highlighted by the row 1 injection and lengthened it further proximally. The pattern arising from row 3 (distal calf) injection
is marked with blue lines and is seen overlapping partially with the level 1 and level 2 patterns. The highest level of injection points at 4
(proximal leg) did not show any further linear patterns, and since this was close to the popliteal fossa, no further injections were
necessary.
In patients with advanced lymphedema, the dermal backflow results from reflux of lymph/ICG from
collectors into the precollectors (valved) and lymph capillaries (valveless). This reflux may not be apparent
immediately after injection, but the poor flow gradient hinders the forward flow of ICG injected distal to
such zones. This will be seen as interrupted linear pattern in ICG lymphography. To allow ICG to re-enter
the lymphatic channels and resume antegrade flow, it is injected anatomically proximal to such an area of
linear pattern interruption [Figure 2] .
[9]
In keeping with the lymphosome theory, multiple, distal-level injection techniques have been described by
some authors to include more lymhosomes [8,10-12] . However, within the length of a given lymphosome, there
can be segments of unfavorable flow. Our technique allows the inclusion of all relevant lymphosomes as
well as overcomes barriers to ICG antegrade flow within a lymphosome by injecting both distal and
proximal to it.
CONCLUSION
The described distal- to- proximal sequential ICG injection technique (DOPSIT) enhances the
intraoperative lymphatic mapping capability of ICG lymphography and facilitates successful LVA.