Page 25 - Read Online
P. 25
Toscano et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2021;8:14-41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2020.12 Page 21
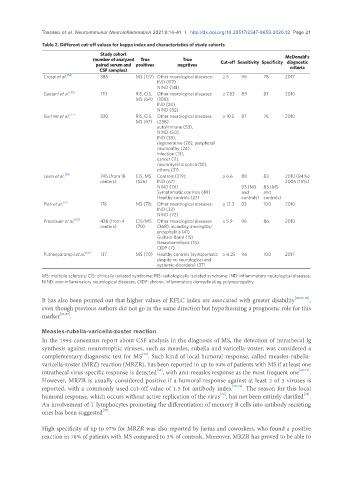
Table 2. Different cut-off values for kappa index and characteristics of study cohorts
Study cohort
(number of analyzed True True McDonald’s
paired serum and positives negatives Cut-off Sensitivity Specificity diagnostic
CSF samples) criteria
Crespi et al. [54] 385 MS (127) Other neurological diseases: ≥ 5 96 78 2017
IND (117)
NIND (141)
Gaetani et al. [56] 170 RIS, CIS, Other neurological diseases ≥ 7.83 89 81 2010
MS (64) (106):
IND (24)
NIND (82)
Gurtner et al. [57] 320 RIS, CIS, Other neurological diseases ≥ 10.5 87 76 2010
MS (67) (258):
autoimmune (53),
NIND (50),
IND (38),
degenerative (28), peripheral
neuropathy (24),
infection (13),
cancer (11),
neuromyelitis optica (10),
others (31)
Leurs et al. [59] 745 (from 18 CIS, MS Controls (219): ≥ 6.6 88 83 2010 (84%)
centers) (526) IND (67) 2005 (16%)
NIND (76) 93 (MS 83 (MS
Symptomatic controls (49) and and
Healthy controls (27) controls) controls)
Pieri et al. [53] 176 MS (71) Other neurological diseases: ≥ 12.3 93 100 2010
IND (33)
NIND (72)
Presslauer et al. [58] 438 (from 4 CIS/MS Other neurological diseases ≥ 5.9 96 86 2010
centers) (70) (368), including meningitis/
encephalitis (41)
Guillain-Barré (15)
Neuroborreliosis (15)
CIDP (7)
Puthenparampil et al. [55] 137 MS (70) Healthy controls (symtpomatic ≥ 4.25 94 100 2017
despite no neurological and
systemic disorders) (37)
MS: multiple sclerosis; CIS: clinically isolated syndrome; RIS: radiologically isolated syndrome; IND: inflammatory neurological diseases;
NIND: non-inflammatory neurological diseases; CIDP: chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
It has also been pointed out that higher values of KFLC index are associated with greater disability [60,64-66] ,
even though previous authors did not go in the same direction but hypothesizing a prognostic role for this
marker [61,67] .
Measles-rubella-varicella-zoster reaction
In the 1994 consensus report about CSF analysis in the diagnosis of MS, the detection of intrathecal Ig
synthesis against neurotrophic viruses, such as measles, rubella and varicella-zoster, was considered a
[18]
complementary diagnostic test for MS . Such kind of local humoral response, called measles-rubella-
varicella-zoster (MRZ) reaction (MRZR), has been reported in up to 94% of patients with MS if at least one
[68]
intrathecal virus-specific response is detected , with anti-measles response as the most frequent one [69-71] .
However, MRZR is usually considered positive if a humoral response against at least 2 of 3 viruses is
reported, with a commonly used cut-off value of 1.5 for antibody index [72,73] . The reason for this local
[74]
[75]
humoral response, which occurs without active replication of the virus , has not been entirely clarified .
An involvement of T lymphocytes promoting the differentiation of memory B cells into antibody secreting
[70]
ones has been suggested .
High specificity of up to 97% for MRZR was also reported by Jarius and coworkers, who found a positive
reaction in 78% of patients with MS compared to 3% of controls. Moreover, MRZR has proved to be able to