Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
Page 16 Toscano et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2021;8:14-41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2020.12
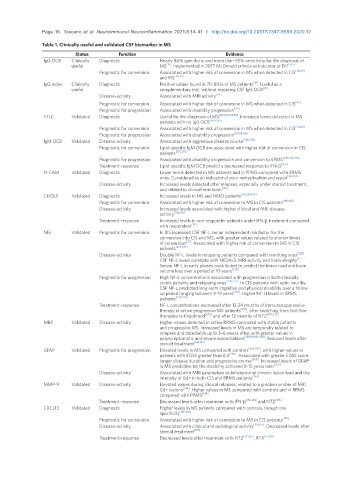
Table 1. Clinically useful and validated CSF biomarker in MS
Status Function Evidence
IgG OCB Clinically Diagnostic Nearly 86% specificity and more than 95% sensitivity for the diagnosis of
useful MS [19] . Implemented in 2017 McDonald criteria as indicator of DIT [20]
Prognostic for conversion Associated with higher risk of conversion in MS when detected in CIS [28,29]
and RIS [30-32]
IgG index Clinically Diagnostic Positive values found in 70-80% of MS patients [18] . Useful as a
useful complementary tool, without replacing CSF IgG OCB [41]
Disease-activity Associated with MRI activity [45]
Prognostic for conversion Associated with higher risk of conversion in MS when detected in CIS [43]
Prognostic for progression Associated with disability progression [44]
KFLC Validated Diagnostic Useful for the diagnosis of MS [49,51,53,54,58] . Increased levels detected in MS
patients with no IgG OCB [50,55,62]
Prognostic for conversion Associated with higher risk of conversion in MS when detected in CIS [43,60]
Prognostic for progression Associated with disability progression [60,64-66]
IgM OCB Validated Disease-activity Associated with aggressive disease course [248,250]
Prognostic for conversion Lipid-specific IgM OCB are associated with higher risk of conversion in CIS
patients [252,253]
Prognostic for progression Associated with disability progression and conversion to SPMS [247,248,256]
Treatment-response Lipid-specific IgM OCB predict a decreased response to IFN-β [256]
N-CAM Validated Diagnostic Lower levels detected in MS patients and in PPMS compared with RRMS
ones. Considered as an indicator of poor remyelination and repair [180,181]
Disease-activity Increased levels detected after relapses, especially under steroid treatment,
and related to clinical remission [183]
CHI3L1 Validated Diagnostic Increased levels in MS and NMO patients [185,188,189]
Prognostic for conversion Associated with higher risk of conversion to MS in CIS patients [190,192]
Disease-activity Increased levels associated with higher clinical and MRI disease-
activity [190,193]
Treatment-response Increased levels in non-responder patients under IFN-β treatment compared
with responders [193]
NFs Validated Prognostic for conversion In RIS increased CSF NF-L are an independent risk factor for the
conversion into CIS and MS, with greater values related to shorter times
of conversion [32] . Associated with higher risk of conversion to MS in CIS
patients [224,234]
Disease-activity Double NF-L levels in relapsing patients compared with remitting ones [228] .
[11]
CSF NF-L levels correlate with NEDA-3, MRI activity and brain atrophy .
Serum NF-L in early phases contributed to predict the lesion load and brain
volume loss over a period of 10 years [238]
Prognostic for progression High NF-L concentrations associated with progression in both clinically
stable patients and relapsing ones [226,227] . In CIS patients with optic neuritis,
CSF NF-L predicted long-term cognitive and physical disability over a follow-
up period ranging between 9-19 years [235] . Higher NF-H levels in SPMS
patients [224,225]
Treatment-response NF-L concentrations decreased after 12-24 months of immunosuppressive
therapy in active progressive MS patients [239] , after switching from first-line
therapies to fingolimod [240] and after 12 months of NTZ [241,242]
MBP Validated Disease-activity Higher values detected in active RRMS compared with stable patients
and progressive MS. Increased levels in MS are temporally related to
relapses and detectable up to 5-6 weeks after, with greater values in
polysymptomatic and severe exacerbations [158,159,166-168] . Reduced levels after
steroid treatment [168,169]
GFAP Validated Prognostic for progression Elevated levels in MS compared with controls [265-267] , with higher values in
patients with EDSS greater than 6.5 [266] . Associated with greater EDSS score,
longer disease duration and progressive course [268] . Increased levels of GFAP
in MS predictive for the disability achieved 8-10 years later [267]
Disease-activity Associated with MRI parameters as infratentorial chronic lesion load and the
intensity of Gd+ in both CIS and RRMS patients [269]
MMP-9 Validated Disease-activity Elevated values during clinical relapses, related to a greater number of MRI
Gd+ lesions [144] . Higher values in MS compared with controls and in RRMS
compared with PPMS [148]
Treatment-response Decreased levels after treatment with IFN-β [152-154] and NTZ [155]
CXCL13 Validated Diagnostic Higher levels in MS patients compared with controls, though low
specificity [126-128]
Prognostic for conversion Associated with higher risk of conversion to MS in CIS patients [130]
Disease-activity Associated with clinical and radiological activity [126,127] . Decreased levels after
steroid treatment [127]
Treatment-response Decreased levels after treatment with NTZ [127,132] , RTX [129,131]