Page 76 - Read Online
P. 76
Page 4 of 7 Qu et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.01
Palmitate miR-126
JNK Cell
death
TRAF7
ROS DNA
TNF TNFR fragmentation
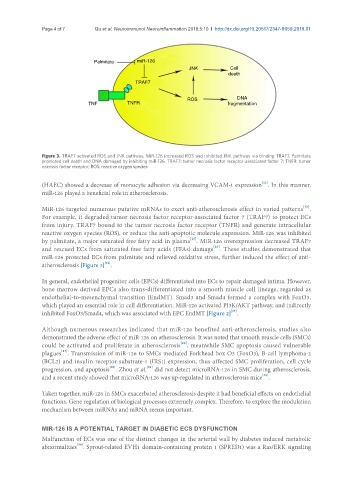
Figure 3. TRAF7 activated ROS and JNK pathway. MiR-126 increased ROS and inhibited JNK pathway via binding TRAF7. Palmitate
promoted cell death and DNA damaged by inhibiting miR-126. TRAF7: tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 7; TNFR: tumor
necrosis factor receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species
[22]
(HAEC) showed a decrease of monocyte adhesion via decreasing VCAM-1 expression . In this manner,
miR-126 played a beneficial role in atherosclerosis.
[18]
MiR-126 targeted numerous putative mRNAs to exert anti-atherosclerosis effect in varied patterns .
For example, it degraded tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 7 (TRAF7) to protect ECs
from injury. TRAF7 bound to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) and generate intracellular
reactive oxygen species (ROS), or reduce the anti-apoptotic molecule expression. MiR-126 was inhibited
[23]
by palmitate, a major saturated free fatty acid in plasma . MiR-126 overexpression decreased TRAF7
[23]
and rescued ECs from saturated free fatty acids (FFAs) damage . These studies demonstrated that
miR-126 protected ECs from palmitate and relieved oxidative stress, further induced the effect of anti-
[24]
atherosclerosis [Figure 3] .
In general, endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) differentiated into ECs to repair damaged intima. However,
bone marrow derived EPCs also trans-differentiated into a smooth muscle cell lineage, regarded as
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT). Smad3 and Smad4 formed a complex with FoxO3,
which played an essential role in cell differentiation. MiR-126 activated PI3K/AKT pathway, and indirectly
[25]
inhibited FoxO3/Smad4, which was associated with EPC EndMT [Figure 2] .
Although numerous researches indicated that miR-126 benefited anti-atherosclerosis, studies also
demonstrated the adverse effect of miR-126 on atherosclerosis. It was noted that smooth muscle cells (SMCs)
[26]
could be activated and proliferate in atherosclerosis , meanwhile SMC apoptosis caused vulnerable
[27]
plagues . Transmission of miR-126 to SMCs mediated Forkhead box O3 (FoxO3), B-cell lymphoma-2
(BCL2) and insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS1) expression, thus affected SMC proliferation, cell cycle
[28]
[28]
progression, and apoptosis . Zhou et al. did not detect microRNA-126 in SMC during atherosclerosis,
[29]
and a recent study showed that microRNA-126 was up-regulated in atherosclerosis mice .
Taken together, miR-126 in SMCs exacerbated atherosclerosis despite it had beneficial effects on endothelial
functions. Gene regulation of biological processes extremely complex. Therefore, to explore the modulation
mechanism between miRNAs and mRNA seems important.
MIR-126 IS A POTENTIAL TARGET IN DIABETIC ECS DYSFUNCTION
Malfunction of ECs was one of the distinct changes in the arterial wall by diabetes induced metabolic
[30]
abnormalities . Sprout-related EVH1 domain-containing protein 1 (SPRED1) was a Ras/ERK signaling