Page 75 - Read Online
P. 75
Qu et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.01 Page 3 of 7
miR-126 TGFb
EndMT
TGFbR
PIK3R2
Smad4/FoxO3
PI3K AKT
VEGF
VEGFR
Angiogenesis
MAPK ERK
SPRED1
miR-126
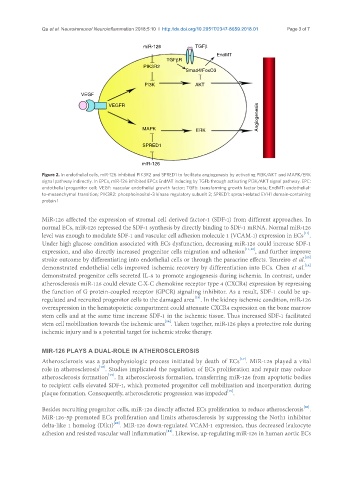
Figure 2. In endothelial cells, miR-126 inhibited PIK3R2 and SPRED1 to facilitate angiogenesis by activating PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK
signal pathway indirectly. In EPCs, miR-126 inhibited EPCs EndMT inducing by TGFb through activating PI3K/AKT signal pathway. EPC:
endothelial progenitor cell; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; TGFb: transforming growth factor beta; EndMT: endothelial-
to-mesenchymal transition; PIK3R2: phosphoinositol-3 kinase regulatory subunit 2; SPRED1: sprout-related EVH1 domain-containing
protein 1
MiR-126 affected the expression of stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) from different approaches. In
normal ECs, miR-126 repressed the SDF-1 synthesis by directly binding to SDF-1 mRNA. Normal miR-126
[11]
level was enough to modulate SDF-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) expression in ECs .
Under high glucose condition associated with ECs dysfunction, decreasing miR-126 could increase SDF-1
expression, and also directly increased progenitor cells migration and adhesion [11,12] , and further improve
[13]
stroke outcome by differentiating into endothelial cells or through the paracrine effects. Tenreiro et al.
[14]
demonstrated endothelial cells improved ischemic recovery by differentiation into ECs. Chen et al.
demonstrated progenitor cells secreted IL-8 to promote angiogenesis during ischemia. In contrast, under
atherosclerosis miR-126 could elevate C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) expression by repressing
the function of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling inhibitor. As a result, SDF-1 could be up-
[15]
regulated and recruited progenitor cells to the damaged area . In the kidney ischemic condition, miR-126
overexpression in the hematopoietic compartment could attenuate CXCR4 expression on the bone marrow
stem cells and at the same time increase SDF-1 in the ischemic tissue. Thus increased SDF-1 facilitated
[16]
stem cell mobilization towards the ischemic area . Taken together, miR-126 plays a protective role during
ischemic injury and is a potential target for ischemic stroke therapy.
MIR-126 PLAYS A DUAL-ROLE IN ATHEROSCLEROSIS
[17]
Atherosclerosis was a pathophysiologic process initiated by death of ECs . MiR-126 played a vital
[18]
role in atherosclerosis . Studies implicated the regulation of ECs proliferation and repair may reduce
[19]
atherosclerosis formation . In atherosclerosis formation, transferring miR-126 from apoptotic bodies
to recipient cells elevated SDF-1, which promoted progenitor cell mobilization and incorporation during
[15]
plaque formation. Consequently, atherosclerotic progression was impeded .
[20]
Besides recruiting progenitor cells, miR-126 directly affected ECs proliferation to reduce atherosclerosis .
MiR-126-5p promoted ECs proliferation and limits atherosclerosis by suppressing the Noth1 inhibitor
[20]
delta-like 1 homolog (Dlk1) . MiR-126 down-regulated VCAM-1 expression, thus decreased leukocyte
[21]
adhesion and resisted vascular wall inflammation . Likewise, up-regulating miR-126 in human aortic ECs