Page 381 - Read Online
P. 381
Yelton et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.58 Page 11 of 18
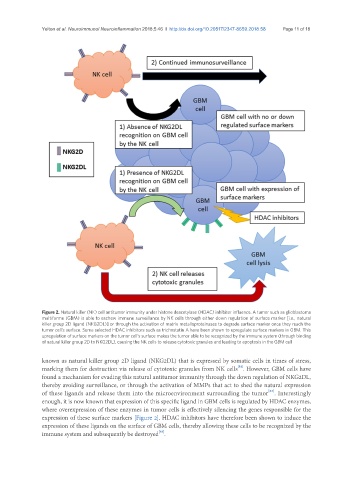
Figure 2. Natural killer (NK) cell antitumor immunity under histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor influence. A tumor such as glioblastoma
multiforme (GBM) is able to eschew immune surveillance by NK cells through either down regulation of surface marker [i.e., natural
killer group 2D ligand (NKG2DL)] or through the activation of matrix metalloproteinases to degrade surface marker once they reach the
tumor cell’s surface. Some selected HDAC inhibitors such as trichostatin A have been shown to upregulate surface markers in GBM. This
upregulation of surface markers on the tumor cell’s surface makes the tumor able to be recognized by the immune system (through binding
of natural killer group 2D to NKG2DL), causing the NK cells to release cytotoxic granules and leading to apoptosis in the GBM cell
known as natural killer group 2D ligand (NKG2DL) that is expressed by somatic cells in times of stress,
[81]
marking them for destruction via release of cytotoxic granules from NK cells . However, GBM cells have
found a mechanism for evading this natural antitumor immunity through the down regulation of NKG2DL,
thereby avoiding surveillance, or through the activation of MMPs that act to shed the natural expression
[82]
of these ligands and release them into the microenvironment surrounding the tumor . Interestingly
enough, it is now known that expression of this specific ligand in GBM cells is regulated by HDAC enzymes,
where overexpression of these enzymes in tumor cells is effectively silencing the genes responsible for the
expression of these surface markers [Figure 2]. HDAC inhibitors have therefore been shown to induce the
expression of these ligands on the surface of GBM cells, thereby allowing these cells to be recognized by the
[83]
immune system and subsequently be destroyed .