Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Page 4 of 13 Fearon et al. Metab Target Organ Damage 2022;2:13 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mtod.2022.12
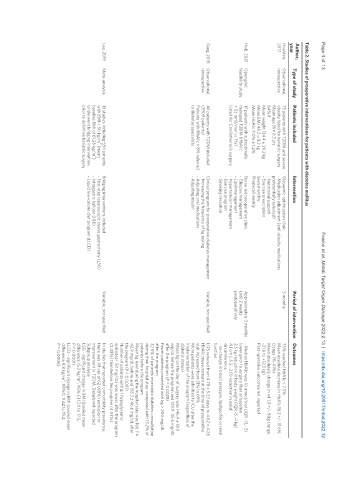
Table 2. Studies of preoperative interventions for patients with diabetes mellitus
Author, Type of study Patients included Intervention Period of intervention Outcomes
year
Houlden, Observational, 75 patients with T2DM and severe Glycaemic optimization clinic 5 months 75% reached HbA1c < 7.5%
2017 retrospective obesity listed for bariatric surgery - Medication adjustment (anti-obesity medications Mean absolute decrease in HbA1c 18.2 +/- 11.6%
Mean age 51 ± 8.3 yrs preferentially selected) (range 1%-41%)
64% F - Nutritional support Mean absolutely change in wt 1.9 +/- 8 kg (range
Mean weight 134.4 ± 29.2 kg - Exercise prescription -31.6 to +12.3 kg)
Mean BMI 48.2 ± 8.3 kg Seen monthly Post-operative outcomes not reported
Mean HbA1c 9.0% ± 1.2% Phonecall weekly
Holt, 2021 Open pilot 17 patients with suboptimally Nurse-led preoperative clinic Approximately 3 months - Median HbA1c was 10 mmol/mol (IQR -13, -3)
feasibility study managed T2DM (HbA1c - Glucose management until 2 weeks lower prior to surgery than at baseline
> 53 mml/mol or 7%) - Lipid management postoperatively 2.5 kg reduction in body weight (IQR -5, -1 kg)
Listed for Cardiothoracic surgery - Hypertension management 4.1 cm (-5.3, -2.0) reduction in waist
- Exercise program circumference
- Smoking cessation - no change in blood pressure, lipid profile or renal
function
Garg, 2018 Observational, All patients with T2DM included Clinical program for preoperative diabetes management Variable, not specified LOS reduced from 4.78 ± 5.23 days to 4.62 ± 4.28
retrospective (3909 patients) - Increasing the frequency of bg testing HbA1c measurement at the time of preoperative
Patients with HbA1c > 8% referred - Adjusting oral medications visit increased from 31% to 69%
to diabetes specialists - Adjusting insulin More patients were admitted to ICU after the
implementation of the program (regardless of
diabetic status)
Mean bg on the day of surgery was 146.4 ± 51.9
mg/dL before the program and 139.9 45.6 mg/dL
after the program (P = 0.0028)
Fewer patients presented with bg > 200 mg/dL
after the program
32.5% of patients received a diabetes consultation
during their hospital stay, compared with 13.2% of
patients before the program
Mean bg level during the hospital stay was 166.7 ±
42.9 mg/dL before and 158.3 ± 46.6 mg/dL after
the program (P < 0.0001)
Number of patients with ≥ 1 hypoglycemic
episode(< 50 mg/dL) was lower after the program
(2.48%) than before the program (4.93%)
Lee, 2019 Meta-analysis 13 studies including 550 patients Bridging interventions included Variable, not specified In studies that reported comorbidity prevalence,
2
with BMI > 50 kg/m (mean - First-step laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) there was 48 out of 62 (68%) remission or
2
baseline BMI of 61.26 kg/m ) - Intragastric balloon (IGB) improvement in T2DM. Details not reported
Underwent bridging intervention - Liquid low-calorie diet program (LLCD) Subgroup analysis
prior to definitive bariatric surgery LSG - significant change in BMI (pooled mean
2
difference 15.2 kg/m , 95% CI 12.9 to 17.5,
P < 0.0001)
LLCD - significant change in BMI (pooled mean
2
difference 9.8 kg/m , 95%CI 9.82 to 15.4,
P = 0.0006)