Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
Mathieu et al. Metab Target Organ Damage 2022;2:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mtod.2022.16 Page 5 of 11
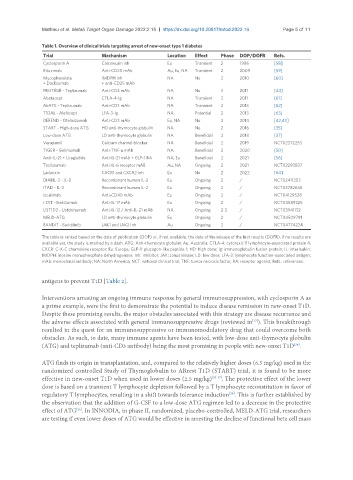
Table 1. Overview of clinical trials targeting arrest of new-onset type 1 diabetes
Trial Mechanism Location Effect Phase DOP/DOFR Refs.
Cyclosporin A Calcineurin inh Eu Transient 2 1986 [58]
Rituximab Anti-CD20 mAb Au, Eu, NA Transient 2 2009 [59]
Mycophenolate IMDPH inh NA No 2 2010 [60]
+ Daclizumab + anti-CD25 mAb
PROTÉGÉ - Teplizumab Anti-CD3 mAb NA No 3 2011 [44]
Abatacept CTLA-4-Ig NA Transient 2 2011 [61]
AbATE - Teplizumab Anti-CD3 mAb NA Transient 2 2013 [62]
T1DAL - Alefacept LFA-3-Ig NA Potential 2 2013 [63]
DEFEND - Otelixizumab Anti-CD3 mAb Eu, NA No 3 2014 [42,43]
START - High-dose ATG HD anti-thymocyte globulin NA No 2 2016 [35]
Low-dose ATG LD anti-thymocyte globulin NA Beneficial 2 2018 [37]
Verapamil Calcium channel-blocker NA Beneficial 2 2019 NCT02372253
T1GER - Golimumab Anti-TNF-α mAb NA Beneficial 2 2020 [50]
Anti-IL-21 + Liraglutide Anti-IL-21 mAb + GLP-1 RA NA, Eu Beneficial 2 2021 [56]
Tocilizumab Anti-IL-6 receptor mAB Au, NA Ongoing 2 2021 NCT02293837
Ladarixin CXCR1 and CXCR2 Inh Eu No 2 2022 [64]
DIABIL-2 - IL-2 Recombinant human IL-2 Eu Ongoing 2 / NCT02411253
ITAD - IL-2 Recombinant human IL-2 Eu Ongoing 2 / NCT03782636
Iscalimab Anti-CD40 mAb Eu Ongoing 2 / NCT04129528
I-DIT - Ixekizumab Anti-IL-17 mAb Eu Ongoing 2 / NCT04589325
UST1D2 - Ustekinumab Anti-IL-12 / Anti-IL-21 mAb NA Ongoing 2-3 / NCT03941132
MELD-ATG LD anti-thymocyte globulin Eu Ongoing 2 / NCT04509791
BANDIT - Baricitinib JAK1 and JAK2 Inh Au Ongoing 2 / NCT04774224
The table is ranked based on the date of publication (DOP) or, if not available, the date of the release of the first results (DOFR). If no results are
available yet, the study is marked by a dash. ATG: Anti-thymocyte globulin; Au: Australia; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4;
CXCR: C-X-C chemokine receptor; Eu: Europe; GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide 1; HD: high dose; Ig: immunoglobulin fusion protein; IL: interleukin;
IMDPH: inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; Inh: inhibitor; JAK: Janus kinase; LD: low dose; LFA-3: lymphocyte function-associated antigen;
mAb: monoclonal antibody; NA: North America; NCT: national clinical trial; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; RA: receptor agonist; Refs.: references.
antigens to prevent T1D [Table 2].
Interventions arresting an ongoing immune response by general immunosuppression, with cyclosporin A as
a prime example, were the first to demonstrate the potential to induce disease remission in new-onset T1D.
Despite these promising results, the major obstacles associated with this strategy are disease recurrence and
the adverse effects associated with general immunosuppressive drugs (reviewed in ). This breakthrough
[33]
resulted in the quest for an immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory drug that could overcome both
obstacles. As such, to date, many immune agents have been tested, with low-dose anti-thymocyte globulin
(ATG) and teplizumab (anti-CD3 antibody) being the most promising in people with new-onset T1D .
[34]
ATG finds its origin in transplantation, and, compared to the relatively higher doses (6.5 mg/kg) used in the
randomized controlled Study of Thymoglobulin to ARrest T1D (START) trial, it is found to be more
effective in new-onset T1D when used in lower doses (2.5 mg/kg) [35-37] . The protective effect of the lower
dose is based on a transient T lymphocyte depletion followed by a T lymphocyte reconstitution in favor of
[38]
regulatory T lymphocytes, resulting in a shift towards tolerance induction . This is further established by
the observation that the addition of G-CSF to a low-dose ATG regimen led to a decrease in the protective
effect of ATG . In INNODIA, in phase II, randomized, placebo-controlled, MELD-ATG trial, researchers
[36]
are testing if even lower doses of ATG would be effective in arresting the decline of functional beta cell mass