Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Iruzubieta et al. Metab Target Organ Damage. 2025;5:10 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mtod.2024.143 Page 11 of 16
Table 1. Key strategies for implementing MASLD in healthcare systems
Implementation area Recommended steps
Education and training -Implement targeted educational programs for healthcare professionals (primary care, hepatology,
endocrinology) to ensure they understand MASLD’s diagnostic criteria and implications
-Develop online resources, workshops, and continuing medical education activities to facilitate
knowledge dissemination
Standardization of diagnostic protocols -Establish clear clinical guidelines to ensure uniform MASLD diagnosis
-Prioritize the use of non-invasive tools (FIB-4, transient elastography), making MASLD evaluation more
accessible
Integration into International and -Advocate for ICD-11 updates to incorporate MASLD
National Coding Systems -Provide guidance for policymakers and healthcare administrators on updating electronic records while
ensuring data continuity
Public health initiatives and awareness -Launch awareness campaigns to educate patients and reduce confusion about the terminology change
campaigns -Develop patient-friendly materials to improve engagement and promote early screening
Adaptation for resource-limited -Focus on cost-effective screening approaches, prioritizing metabolic risk assessment in primary care
settings -Leverage telemedicine to expand access to education and diagnostic support
MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; ICD: International Classification of Diseases.
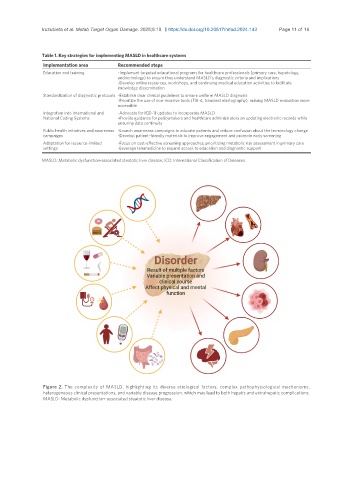
Figure 2. The complexity of MASLD, highlighting its diverse etiological factors, complex pathophysiological mechanisms,
heterogeneous clinical presentations, and variable disease progression, which may lead to both hepatic and extrahepatic complications.
MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.