Page 751 - Read Online
P. 751
Page 20 of 24 Palacios Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:73 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.72
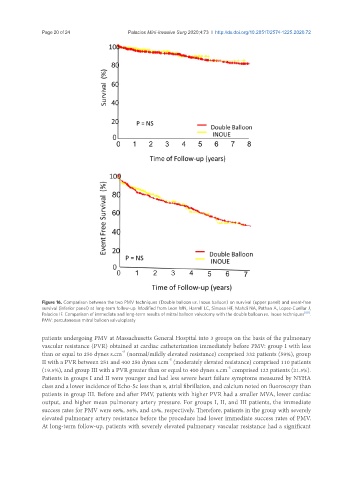
Figure 16. Comparison between the two PMV techniques (Double balloon vs. Inoue balloon) on survival (upper panel) and event-free
survival (inferior panel) at long-term follow-up. Modified from Leon MN, Harrell LC, Simosa HF, Mahdi NA, Pathan A, Lopez-Cuellar J,
Palacios IF. Comparison of immediate and long-term results of mitral balloon valvotomy with the double balloon vs. Inoue techniques [60] .
PMV: percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty
patients undergoing PMV at Massachusetts General Hospital into 3 groups on the basis of the pulmonary
vascular resistance (PVR) obtained at cardiac catheterization immediately before PMV: group I with less
-5
than or equal to 250 dynes s.cm (normal/mildly elevated resistance) comprised 332 patients (59%), group
-5
II with a PVR between 251 and 400 250 dynes s.cm (moderately elevated resistance) comprised 110 patients
-5
(19.5%), and group III with a PVR greater than or equal to 400 dynes s.cm comprised 122 patients (21.5%).
Patients in groups I and II were younger and had less severe heart failure symptoms measured by NYHA
class and a lower incidence of Echo-Sc less than 8, atrial fibrillation, and calcium noted on fluoroscopy than
patients in group III. Before and after PMV, patients with higher PVR had a smaller MVA, lower cardiac
output, and higher mean pulmonary artery pressure. For groups I, II, and III patients, the immediate
success rates for PMV were 68%, 56%, and 45%, respectively. Therefore, patients in the group with severely
elevated pulmonary artery resistance before the procedure had lower immediate success rates of PMV.
At long-term follow-up, patients with severely elevated pulmonary vascular resistance had a significant