Page 290 - Read Online
P. 290
Mansy et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2018;2:36 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.48 Page 3 of 9
A B
C D
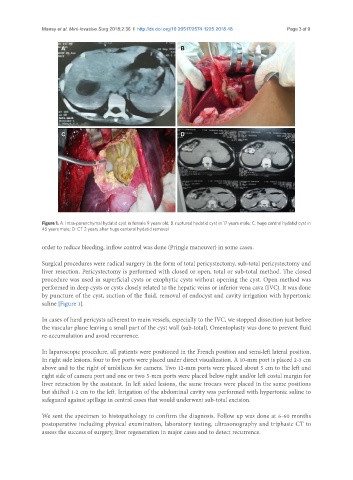
Figure 1. A: Intra-parenchymal hydatid cyst in female 9 years old; B: ruptured hydatid cyst in 17 years male; C: huge central hydatid cyst in
45 years male; D: CT 2 years after huge centeral hydatid removal
order to reduce bleeding, inflow control was done (Pringle maneuver) in some cases.
Surgical procedures were radical surgery in the form of total pericystectomy, sub-total pericystectomy and
liver resection. Pericystectomy is performed with closed or open, total or sub-total method. The closed
procedure was used in superficial cysts or exophytic cysts without opening the cyst. Open method was
performed in deep cysts or cysts closely related to the hepatic veins or inferior vena cava (IVC). It was done
by puncture of the cyst, suction of the fluid, removal of endocyst and cavity irrigation with hypertonic
saline [Figure 1].
In cases of hard pericysts adherent to main vessels, especially to the IVC, we stopped dissection just before
the vascular plane leaving a small part of the cyst wall (sub-total). Omentoplasty was done to prevent fluid
re-accumulation and avoid recurrence.
In laparoscopic procedure, all patients were positioned in the French position and semi-left lateral position.
In right side lesions, four to five ports were placed under direct visualization. A 10-mm port is placed 2-3 cm
above and to the right of umbilicus for camera. Two 12-mm ports were placed about 5 cm to the left and
right side of camera port and one or two 5-mm ports were placed below right and/or left costal margin for
liver retraction by the assistant. In left sided lesions, the same trocars were placed in the same positions
but shifted 1-2 cm to the left. Irrigation of the abdominal cavity was performed with hypertonic saline to
safeguard against spillage in central cases that would underwent sub-total excision.
We sent the specimen to histopathology to confirm the diagnosis. Follow up was done at 6-60 months
postoperative including physical examination, laboratory testing, ultrasonography and triphasic CT to
assess the success of surgery, liver regeneration in major cases and to detect recurrence.