Page 217 - Read Online
P. 217
Riaz et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2018;2:28 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.41 Page 7 of 8
Table 1. Dominant vs. non-dominant hand, baseline and final results in both groups
Task: performing hand Assessment stage Groups Mean ± 2 sem t-test
Control 0.94 ± 0.09
Baseline Mental Training 1.07 ± 0.14 P = 0.4
Dominant hand
Control 1.06 ± 0.14
Final P = 0.01
Mental Training 0.66 ± 0.04
Control 1.10 ± 0.12
Baseline P = 0.8
Mental Training 1.04 ± 0.12
Non-dominant hand Control 1.10 ± 0.20
Final P = 0.04
Mental Training 0.73 ± 0.04
1.75 Control
Mental training
1.50
= P < 0.05 vs. Control
Final task (kg) 1.00
1.25
0.75
0.50
Dominat Non-dominat
Hand
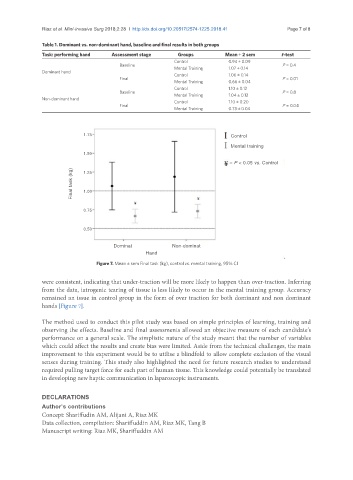
Figure 7. Mean ± sem Final task (kg), control vs. mental training, 95% CI
were consistent, indicating that under-traction will be more likely to happen than over-traction. Inferring
from the data, iatrogenic tearing of tissue is less likely to occur in the mental training group. Accuracy
remained an issue in control group in the form of over traction for both dominant and non dominant
hands [Figure 7].
The method used to conduct this pilot study was based on simple principles of learning, training and
observing the effects. Baseline and final assessments allowed an objective measure of each candidate’s
performance on a general scale. The simplistic nature of the study meant that the number of variables
which could affect the results and create bias were limited. Aside from the technical challenges, the main
improvement to this experiment would be to utilise a blindfold to allow complete exclusion of the visual
senses during training. This study also highlighted the need for future research studies to understand
required pulling target force for each part of human tissue. This knowledge could potentially be translated
in developing new haptic communication in laparoscopic instruments.
DECLARATIONS
Author’s contributions
Concept: Shariffudin AM, Alijani A, Riaz MK
Data collection, compilation: Shariffuddin AM, Riaz MK, Tang B
Manuscript writing: Riaz MK, Shariffuddin AM