Page 66 - Read Online
P. 66
Koga et al. Minimal laminectomy with the interlaminar approach for PELD
preoperative and postoperative radiological changes in case 12, in which we removed the SAP and cephalic
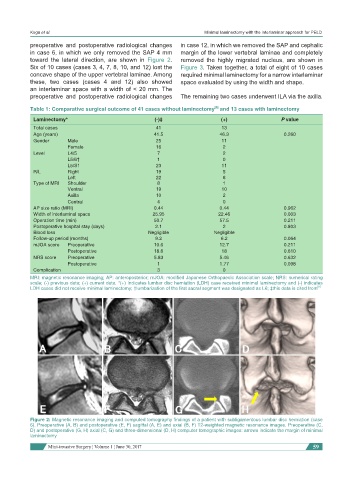
in case 6, in which we only removed the SAP 4 mm margin of the lower vertebral laminae and completely
toward the lateral direction, are shown in Figure 2. removed the highly migrated nucleus, are shown in
Six of 10 cases (cases 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, and 12) lost the Figure 3. Taken together, a total of eight of 10 cases
concave shape of the upper vertebral laminae. Among required minimal laminectomy for a narrow interlaminar
these, two cases (cases 4 and 12) also showed space evaluated by using the width and shape.
an interlaminar space with a width of < 20 mm. The
preoperative and postoperative radiological changes The remaining two cases underwent ILA via the axilla.
[8]
Table 1: Comparative surgical outcome of 41 cases without laminectomy and 13 cases with laminectomy
Laminectomy* (-)‡ (+) P value
Total cases 41 13
Age (years) 41.5 46.3 0.260
Gender Male 25 11
Female 16 2
Level L4/5 7 2
L5/6† 1 0
L5/S1 23 11
R/L Right 19 5
Left 22 8
Type of MRI Shoulder 8 1
Ventral 19 10
Axilla 10 2
Central 4 0
AP size ratio (MRI) 0.44 0.44 0.962
Width of interlaminal space 25.95 22.46 0.003
Operation time (min) 50.7 57.5 0.211
Postoperative hospital stay (days) 2.1 2 0.803
Blood loss Negligible Negligible
Follow-up period (months) 9.2 6.2 0.064
mJOA score Preoperative 10.6 12.7 0.211
Postoperative 18.6 18 0.610
NRS score Preoperative 5.83 5.46 0.632
Postoperative 1 1.77 0.098
Complication 3 0
MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; AP: anteroposterior; mJOA: modified Japanese Orthopaedic Association scale; NRS: numerical rating
scale; (-) previous data; (+) current data. *(+) Indicates lumbar disc herniation (LDH) case received minimal laminectomy and (-) indicates
LDH cases did not receive minimal laminectomy; †lumbarization of the first sacral segment was designated as L6; ‡this data is cited from [8]
Figure 2: Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography findings of a patient with subligamentous lumbar disc herniation (case
6). Preoperative (A, B) and postoperative (E, F) sagittal (A, E) and axial (B, F) T2-weighted magnetic resonance images. Preoperative (C,
D) and postoperative (G, H) axial (C, G) and three-dimensional (D, H) computer tomographic images: arrows indicate the margin of minimal
laminectomy
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017 59