Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
Neto et al. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication
A
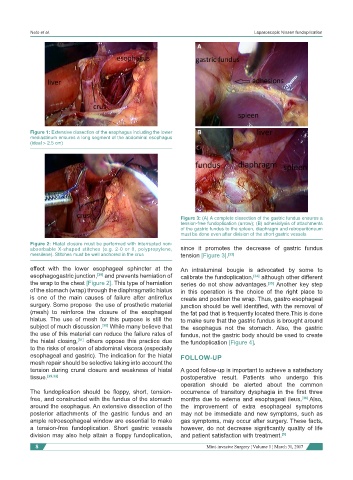
Figure 1: Extensive dissection of the esophagus including the lower B
mediastinum ensures a long segment of the abdominal esophagus
(ideal > 2.5 cm)
Figure 3: (A) A complete dissection of the gastric fundus ensures a
tension-free fundoplication (arrow); (B) adhesiolysis of attachments
of the gastric fundus to the spleen, diaphragm and retroperitoneum
must be done even after division of the short gastric vessels
Figure 2: Hiatal closure must be performed with interrupted non-
absorbable X-shaped stitches (e.g. 2-0 or 0, polypropylene, since it promotes the decrease of gastric fundus
mersilene). Stitches must be well anchored in the crus tension [Figure 3]. [33]
effect with the lower esophageal sphincter at the An intraluminal bougie is advocated by some to
esophagogastric junction, [29] and prevents herniation of calibrate the fundoplication, [34] although other different
the wrap to the chest [Figure 2]. This type of herniation series do not show advantages. [35] Another key step
of the stomach (wrap) through the diaphragmatic hiatus in this operation is the choice of the right place to
is one of the main causes of failure after antireflux create and position the wrap. Thus, gastro esophageal
surgery. Some propose the use of prosthetic material junction should be well identified, with the removal of
(mesh) to reinforce the closure of the esophageal the fat pad that is frequently located there.This is done
hiatus. The use of mesh for this purpose is still the to make sure that the gastric fundus is brought around
subject of much discussion. [30] While many believe that the esophagus not the stomach. Also, the gastric
the use of this material can reduce the failure rates of fundus, not the gastric body should be used to create
the hiatal closing, [31] others oppose this practice due the fundoplication [Figure 4].
to the risks of erosion of abdominal viscera (especially
esophageal and gastric). The indication for the hiatal FOLLOW-UP
mesh repair should be selective taking into account the
tension during crural closure and weakness of hiatal A good follow-up is important to achieve a satisfactory
tissue. [29,32] postoperative result. Patients who undergo this
operation should be alerted about the common
The fundoplication should be floppy, short, tension- occurrence of transitory dysphagia in the first three
free, and constructed with the fundus of the stomach months due to edema and esophageal ileus. [36] Also,
around the esophagus. An extensive dissection of the the improvement of extra esophageal symptoms
posterior attachments of the gastric fundus and an may not be immediate and new symptoms, such as
ample retroesophageal window are essential to make gas symptoms, may occur after surgery. These facts,
a tension-free fundoplication. Short gastric vessels however, do not decrease significantly quality of life
division may also help attain a floppy fundoplication, and patient satisfaction with treatment. [5]
8 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017