Page 66 - Read Online
P. 66
Ninomiya et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2022;6:33 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2022.12 Page 15 of 18
Table 1. Surgical outcomes of the 58 patients who underwent robot-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy
Operation time (min), mean ± SD
Total 609 ± 75
Thorax 309 ± 71
Robot setup time 23.3 ± 7.6
Console time 255 ± 64
Amount of blood loss (mL), mean ± SD
Total 286 ± 187
Thorax 135 ± 126
No. of dissected lymph nodes, mean ± SD
Total 58.3 ± 20.2
Thorax 27.1 ± 9.9
Conversion to thoracotomy, No. (%) 0 (0)
a
Curative resection according to pStage , No. (%)
b
pStage I (n = 18) 17 (94.4)
pStage II (n = 9) 9 (100)
pStage III (n = 17) 9 (100)
pStage IV (n = 14) 8 (71.4)
Total (n = 58) 51 (87.9)
a
Tumor was staged according to the TNM classification of the American Joint Committee on Cancer and the Union Internationale Control le
b
Cancer 8th edition; one case with extensive oral intraepithelial spread within long-segment Barrett’s esophagus showed positive oral margin.
SD: Standard deviation; TNM: tumor nodes metastasis.
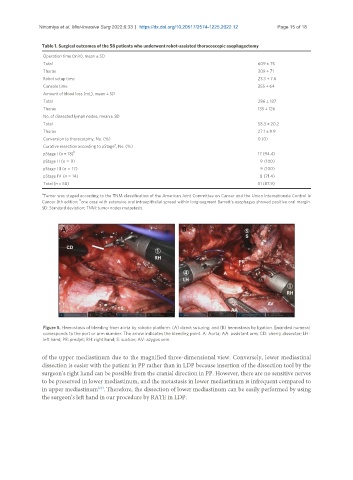
Figure 5. Hemostasis of bleeding from aorta by robotic platform: (A) direct suturing; and (B) hemostasis by ligation. Encircled numeral
corresponds to the port or arm number. The arrow indicates the bleeding point. A: Aorta; AA: assistant arm; CD: cherry dissector; LH:
left hand; PR: predjet; RH: right hand; S: suction; AV: azygos vein.
of the upper mediastinum due to the magnified three-dimensional view. Conversely, lower mediastinal
dissection is easier with the patient in PP rather than in LDP because insertion of the dissection tool by the
surgeon’s right hand can be possible from the cranial direction in PP. However, there are no sensitive nerves
to be preserved in lower mediastinum, and the metastasis in lower mediastinum is infrequent compared to
[29]
in upper mediastinum . Therefore, the dissection of lower mediastinum can be easily performed by using
the surgeon’s left hand in our procedure by RATE in LDP.