Page 106 - Read Online
P. 106
Page 8 of 13 Mauri et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2022;6:49 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2022.34
Table 4. Main trials investigating the best antithrombotic regimen after TAVR in patients with indication to long-term oral
anticoagulant therapy
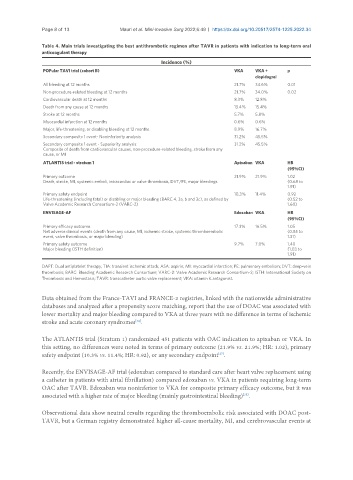
Incidence (%)
POPular TAVI trial (cohort B) VKA VKA + p
clopidogrel
All bleeding at 12 months 21.7% 34.6% 0.01
Non-procedure-related bleeding at 12 months 21.7% 34.0% 0.02
Cardiovascular death at 12 months 8.3% 12.8%
Death from any cause at 12 months 13.4% 15.4%
Stroke at 12 months 5.7% 5.8%
Myocardial infarction at 12 months 0.6% 0.6%
Major, life-threatening, or disabling bleeding at 12 months 8.9% 16.7%
Secondary composite 1 event- Noninferiority analysis 31.2% 45.5%
Secondary composite 1 event - Superiority analysis 31.2% 45.5%
Composite of death from cardiovascular causes, non-procedure-related bleeding, stroke from any
cause, or MI
ATLANTIS trial - stratum 1 Apixaban VKA HR
(95%CI)
Primary outcome 21.9% 21.9% 1.02
Death, stroke, MI, systemic emboli, intracardiac or valve thrombosis, DVT/PE, major bleedings (0.68 to
1.91)
Primary safety endpoint 10.3% 11.4% 0.92
Life-threatening (including fatal) or disabling or major bleeding (BARC 4, 3a, b and 3c), as defined by (0.52 to
Valve Academic Research Consortium-2 (VARC-2) 1.60)
ENVISAGE-AF Edoxaban VKA HR
(95%CI)
Primary efficacy outcome 17.3% 16.5% 1.05
Net adverse clinical events (death from any cause, MI, ischemic stroke, systemic thromboembolic (0.85 to
event, valve thrombosis, or major bleeding) 1.31)
Primary safety outcome 9.7% 7.0% 1.40
Major bleeding (ISTH definition) (1.03 to
1.91)
DAPT: Dual antiplatelet therapy; TIA: transient ischemic attack; ASA: aspirin; MI: myocardial infarction; PE: pulmonary embolism; DVT: deep-vein
thrombosis; BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; VARC-2: Valve Academic Research Consortium-2; ISTH: International Society on
Thrombosis and Hemostasis; TAVR: transcatheter aortic valve replacement; VKA: vitamin K antagonist.
Data obtained from the France-TAVI and FRANCE-2 registries, linked with the nationwide administrative
databases and analyzed after a propensity score matching, report that the use of DOAC was associated with
lower mortality and major bleeding compared to VKA at three years with no difference in terms of ischemic
stroke and acute coronary syndromes .
[34]
The ATLANTIS trial (Stratum 1) randomized 451 patients with OAC indication to apixaban or VKA. In
this setting, no differences were noted in terms of primary outcome (21.9% vs. 21.9%; HR: 1.02), primary
[27]
safety endpoint (10.3% vs. 11.4%; HR: 0.92), or any secondary endpoint .
Recently, the ENVISAGE-AF trial (edoxaban compared to standard care after heart valve replacement using
a catheter in patients with atrial fibrillation) compared edoxaban vs. VKA in patients requiring long-term
OAC after TAVR. Edoxaban was noninferior to VKA for composite primary efficacy outcome, but it was
associated with a higher rate of major bleeding (mainly gastrointestinal bleeding) .
[35]
Observational data show neutral results regarding the thromboembolic risk associated with DOAC post-
TAVR, but a German registry demonstrated higher all-cause mortality, MI, and cerebrovascular events at