Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Lee et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:57 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.139 Page 5 of 10
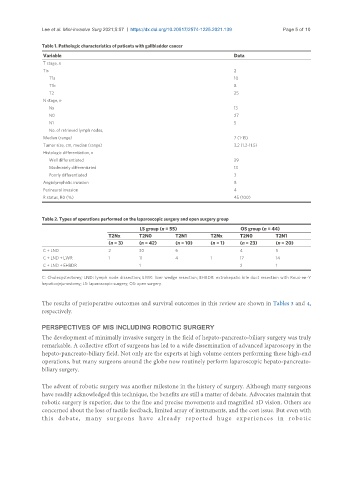
Table 1. Pathologic characteristics of patients with gallbladder cancer
Variable Data
T stage, n
Tis 2
T1a 10
T1b 8
T2 25
N stage, n
Nx 13
N0 27
N1 5
No. of retrieved lymph nodes,
Median (range) 7 (1-15)
Tumor size, cm, median (range) 3.2 (1.2-11.5)
Histologic differentiation, n
Well differentiated 29
Moderately differentiated 13
Poorly differentiated 3
Angiolymphatic invasion 8
Perineural invasion 4
R status, R0 (%) 45 (100)
Table 2. Types of operations performed on the laparoscopic surgery and open surgery group
LS group (n = 55) OS group (n = 44)
T2Nx T2N0 T2N1 T2Nx T2N0 T2N1
(n = 3) (n = 42) (n = 10) (n = 1) (n = 23) (n = 20)
C + LND 2 30 6 4 5
C + LND + LWR 1 11 4 1 17 14
C + LND + EHBDR 1 2 1
C: Cholecystectomy; LND: lymph node dissection; LWR: liver wedge resection; EHBDR: extrahepatic bile duct resection with Roux-en-Y
hepaticojejunostomy; LS: laparoscopic surgery; OS: open surgery.
The results of perioperative outcomes and survival outcomes in this review are shown in Tables 3 and 4,
respectively.
PERSPECTIVES OF MIS INCLUDING ROBOTIC SURGERY
The development of minimally invasive surgery in the field of hepato-pancreato-biliary surgery was truly
remarkable. A collective effort of surgeons has led to a wide dissemination of advanced laparoscopy in the
hepato-pancreato-biliary field. Not only are the experts at high volume centers performing these high-end
operations, but many surgeons around the globe now routinely perform laparoscopic hepato-pancreato-
biliary surgery.
The advent of robotic surgery was another milestone in the history of surgery. Although many surgeons
have readily acknowledged this technique, the benefits are still a matter of debate. Advocates maintain that
robotic surgery is superior, due to the fine and precise movements and magnified 3D vision. Others are
concerned about the loss of tactile feedback, limited array of instruments, and the cost issue. But even with
t h i s d e b a t e , m a n y s u r g e o n s h a v e a l r e a d y r e p o r t e d h u g e e x p e r i e n c e s i n r o b o t i c