Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Ishizawa et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:52 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.81 Page 3 of 6
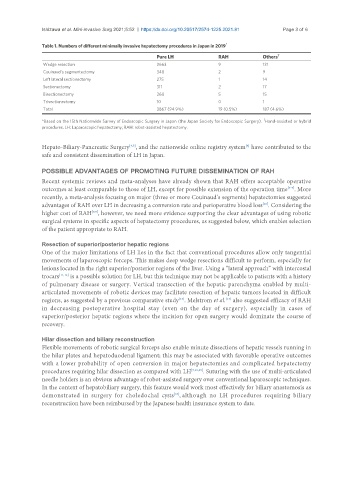
Table 1. Numbers of different minimally invasive hepatectomy procedures in Japan in 2019 *
Pure LH RAH Others †
Wedge resection 2663 9 131
Couinaud’s segmentectomy 348 2 9
Left lateral sectionectomy 275 1 14
Sectionectomy 311 2 17
Bisectionectomy 260 5 15
Trisectionectomy 10 0 1
Total 3867 (94.9%) 19 (0.5%) 187 (4.6%)
†
*Based on the 15th Nationwide Survey of Endoscopic Surgery in Japan (the Japan Society for Endoscopic Surgery). Hand-assisted or hybrid
procedures. LH: Laparoscopic hepatectomy; RAH: robot-assisted hepatectomy.
[6]
[4,5]
Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery , and the nationwide online registry system have contributed to the
safe and consistent dissemination of LH in Japan.
POSSIBLE ADVANTAGES OF PROMOTING FUTURE DISSEMINATION OF RAH
Recent systemic reviews and meta-analyses have already shown that RAH offers acceptable operative
[7-9]
outcomes at least comparable to those of LH, except for possible extension of the operation time . More
recently, a meta-analysis focusing on major (three or more Couinaud’s segments) hepatectomies suggested
advantages of RAH over LH in decreasing a conversion rate and perioperative blood loss . Considering the
[10]
higher cost of RAH , however, we need more evidence supporting the clear advantages of using robotic
[7,9]
surgical systems in specific aspects of hepatectomy procedures, as suggested below, which enables selection
of the patient appropriate to RAH.
Resection of superior/posterior hepatic regions
One of the major limitations of LH lies in the fact that conventional procedures allow only tangential
movements of laparoscopic forceps. This makes deep wedge resections difficult to perform, especially for
lesions located in the right superior/posterior regions of the liver. Using a “lateral approach” with intercostal
trocars [11,12] is a possible solution for LH, but this technique may not be applicable to patients with a history
of pulmonary disease or surgery. Vertical transection of the hepatic parenchyma enabled by multi-
articulated movements of robotic devices may facilitate resection of hepatic tumors located in difficult
regions, as suggested by a previous comparative study . Melstrom et al. also suggested efficacy of RAH
[13]
[14]
in decreasing postoperative hospital stay (even on the day of surgery), especially in cases of
superior/posterior hepatic regions where the incision for open surgery would dominate the course of
recovery.
Hilar dissection and biliary reconstruction
Flexible movements of robotic surgical forceps also enable minute dissections of hepatic vessels running in
the hilar plates and hepatoduodenal ligament; this may be associated with favorable operative outcomes
with a lower probability of open conversion in major hepatectomies and complicated hepatectomy
procedures requiring hilar dissection as compared with LH [7,10,15] . Suturing with the use of multi-articulated
needle holders is an obvious advantage of robot-assisted surgery over conventional laparoscopic techniques.
In the context of hepatobiliary surgery, this feature would work most effectively for biliary anastomosis as
demonstrated in surgery for choledochal cysts , although no LH procedures requiring biliary
[16]
reconstruction have been reimbursed by the Japanese health insurance system to date.