Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Page 4 of 11 Bongiolatti et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.28
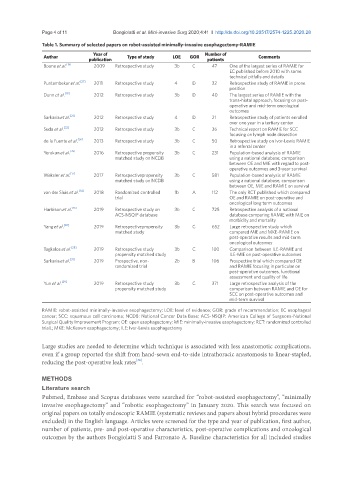
Table 1. Summary of selected papers on robot-assisted minimally-invasive esophagectomy-RAMIE
Year of Number of
Author Type of study LOE GOR Comments
publication patients
Boone et al. [18] 2009 Retrospective study 3b C 47 One of the largest series of RAMIE for
EC published before 2010 with some
technical pitfalls and details
Puntambekar et al. [27] 2011 Retrospective study 4 D 32 Retrospective study of RAMIE in prone
position
Dunn et al. [19] 2012 Retrospective study 3b D 40 The largest series of RAMIE with the
trans-hiatal approach, focusing on post-
operative and mid-term oncological
outcomes
Sarkaria et al. [21] 2012 Retrospective study 4 D 21 Retrospective study of patients enrolled
over one year in a tertiary center
Suda et al. [32] 2012 Retrospective study 3b C 36 Technical report on RAMIE for SCC
focusing on lymph node dissection
de la Fuente et al. [36] 2013 Retrospective study 3b C 50 Retrospective study on Ivor-Lewis RAMIE
in a referral center
Yerokun et al. [39] 2016 Retrospective propensity 3b C 231 Population-based analysis of RAMIE
matched study on NCDB using a national database; comparison
between OE and MIE with regard to post-
operative outcomes and 3-year survival
Weksler et al. [17] 2017 Retrospectivepropensity 3b C 581 Population-based analysis of RAMIE
matched study on NCDB using a national database; comparison
between OE, MIE and RAMIE on survival
van der Sluis et al. [14] 2018 Randomized controlled 1b A 112 The only RCT published which compared
trial OE and RAMIE on post-operative and
oncological long term outcomes
Harbison et al. [16] 2019 Retrospective study on 3b C 725 Retrospective analysis of a national
ACS-NSQIP database database comparing RAMIE with MIE on
morbidity and mortality
Yang et al. [22] 2019 Retrospectivepropensity 3b C 652 Large retrospective study which
matched study compared MIE and MKE-RAMIE on
post-operative results and mid-term
oncological outcomes
Tagkalos et al. [28] 2019 Retrospective study 3b C 100 Comparison between ILE-RAMIE and
propensity matched study ILE-MIE on post-operative outcomes
Sarkaria et al. [31] 2019 Prospective, non- 2b B 106 Prospective trial which compared OE
randomized trial and RAMIE focusing in particular on
post-operative outcomes, functional
assessment and quality of life
Yun et al. [29] 2019 Retrospective study 3b C 371 Large retrospective analysis of the
propensity matched study comparison between RAMIE and OE for
SCC on post-operative outcomes and
mid-term survival
RAMIE: robot-assisted minimally-invasive esophagectomy; LOE: level of evidence; GOR: grade of recommendation; EC esophageal
cancer; SCC: squamous cell carcinoma; NCDB: National Cancer Data Base; ACS-NSQIP: American College of Surgeons-National
Surgical Quality Improvement Program; OE: open esophagectomy; MIE: minimally-invasive esophagectomy; RCT: randomized controlled
trialL; MKE: McKeown esophagectomy; ILE: Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy
Large studies are needed to determine which technique is associated with less anastomotic complications,
even if a group reported the shift from hand-sewn end-to-side intrathoracic anastomosis to linear-stapled,
reducing the post-operative leak rates .
[30]
METHODS
Literature search
Pubmed, Embase and Scopus databases were searched for “robot-assisted esophagectomy”, “minimally
invasive esophagectomy” and “robotic esophagectomy” in January 2020. This search was focused on
original papers on totally endoscopic RAMIE (systematic reviews and papers about hybrid procedures were
excluded) in the English language. Articles were screened for the type and year of publication, first author,
number of patients, pre- and post-operative characteristics, post-operative complications and oncological
outcomes by the authors Bongiolatti S and Farronato A. Baseline characteristics for all included studies