Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Page 4 of 9 Brandolini. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:45 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.27
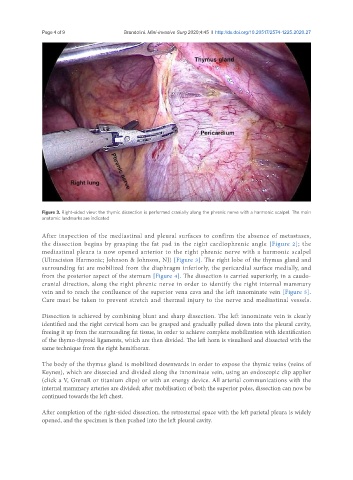
Figure 3. Right-sided view: the thymic dissection is performed cranially along the phrenic nerve with a harmonic scalpel. The main
anatomic landmarks are indicated
After inspection of the mediastinal and pleural surfaces to confirm the absence of metastases,
the dissection begins by grasping the fat pad in the right cardiophrenic angle [Figure 2]; the
mediastinal pleura is now opened anterior to the right phrenic nerve with a harmonic scalpel
(Ultracision Harmonic; Johnson & Johnson, NJ) [Figure 3]. The right lobe of the thymus gland and
surrounding fat are mobilized from the diaphragm inferiorly, the pericardial surface medially, and
from the posterior aspect of the sternum [Figure 4]. The dissection is carried superiorly, in a caudo-
cranial direction, along the right phrenic nerve in order to identify the right internal mammary
vein and to reach the confluence of the superior vena cava and the left innominate vein [Figure 5].
Care must be taken to prevent stretch and thermal injury to the nerve and mediastinal vessels.
Dissection is achieved by combining blunt and sharp dissection. The left innominate vein is clearly
identified and the right cervical horn can be grasped and gradually pulled down into the pleural cavity,
freeing it up from the surrounding fat tissue, in order to achieve complete mobilization with identification
of the thymo-thyroid ligaments, which are then divided. The left horn is visualised and dissected with the
same technique from the right hemithorax.
The body of the thymus gland is mobilized downwards in order to expose the thymic veins (veins of
Keynes), which are dissected and divided along the innominate vein, using an endoscopic clip applier
(click a V, GrenaR or titanium clips) or with an energy device. All arterial communications with the
internal mammary arteries are divided; after mobilisation of both the superior poles, dissection can now be
continued towards the left chest.
After completion of the right-sided dissection, the retrosternal space with the left parietal pleura is widely
opened, and the specimen is then pushed into the left pleural cavity.