Page 70 - Read Online
P. 70
Page 6 of 15 Ruzzenente et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:91 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.90
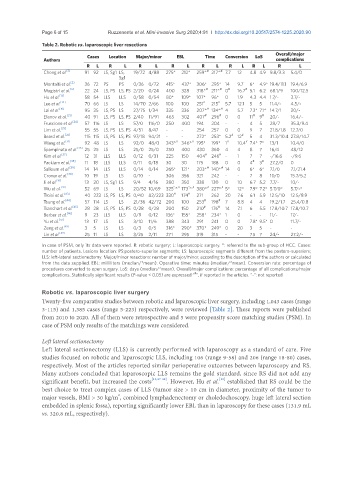
Table 2. Robotic vs. laparoscopic liver resections
Cases Location Major/minor EBL Time Conversion LoS Overall/major
Authors complications
R L R L R L R L R L R L R L R L
Chong et al. [1] 91 92 LS, Sg1 LS, 19/72 4/88 275* 212* 259* ,# 217* ,# 7.7 12 4.8 4.9 9.8/3.3 5.4/0
Sg1
Montalti et al. [2] 36 72 PS PS 0/36 0/72 415* 437* 306* 295* 14 9.7 6* 4.9* 19.4/11.1 19.4/6.9
#
Magistri et al. [6] 22 24 LS, PS LS, PS 2/20 0/24 400 328 318* ,# 211* ,# 0 # 16.7 5.1 6.2 68.1/9 100/12.5
Hu et al. [13] 58 54 LLS LLS 0/58 0/54 80* 109* 107* 96* 0 1.9 4.3 4.4 1.7/- 3.7/-
Lee et al. [14] 70 66 LS LS 14/70 2/66 100 100 251 # 215 # 5.7 12.1 5 5 11.4/- 4.5/-
Lai et al. [16] 95 35 LS, PS LS 27/75 1/34 335 336 207* ,# 134* ,# 4 5.7 7.3* 7.1* 14.7/1 20/-
Efanov et al. [21] 40 91 LS, PS LS, PS 2/40 11/91 465 302 407 # 296 # 0 0 11 # 9 # 20/- 16.4/-
Fruscione et al. [24] 57 116 LS LS 57/0 116/0 250 400 194 204 - - 4 5 28/7 35.3/9.4
Lim et al. [25] 55 55 LS, PS LS, PS 4/51 8/47 - - 254 257 0 0 9 7 21.8/1.8 12.7/0
Beard et al. [26] 115 115 LS, PS LS, PS 97/18 94/21 - - 272* 253* 5.2 # 12 # 5 4 31.3/10.4 27.8/14.7
#
Wang et al. [31] 92 48 LS LS 92/0 48/0 243* ,# 346* ,# 195* 199* 1 # 10.4 7.4* 7* 13/1 10.4/0
Spampinato et al. [36] 25 25 LS LS 25/0 25/0 250 400 430 360 4 4 8 7 16/4 48/12
Kim et al. [37] 12 31 LLS LLS 0/12 0/31 225 150 404 # 246 # - 1 7 7 -/16.6 -/9.6
Packiam et al. [38] 11 18 LLS LLS 0/11 0/18 30 30 175 188 0 0 4 # 3 # 27.2/0 0
,#
Salloum et al. [39] 14 14 LLS LLS 0/14 0/14 265* 121* 203* ,# 140* 14 0 6* 6* 7.1/0 7.1/21.4
Croner et al. [40] 10 19 LS LS 0/10 - 306 356 321 242 - - 7 8 10/0 15.7/5.2
Ji et al. [41] 13 20 LS, Sg1 LS 9/4 4/16 280 350 338 130 0 10 6.7 5.2 7.7/- 10/-
°, ,#
,#
,#
°, ,#
Wu et al. [42] 52 69 LS LS 20/52 10/69 325 * 173 * 380° 227° 5° 12° 7.9° 7.2° 5.7/0° 5.7/-°
Troisi et al. [43] 40 223 LS, PS LS, PS 0/40 82/223 330 # 174 # 271 262 20 7.6 6.1 5.9 12.5/10 12.5/8.9
Tsung et al. [44] 57 114 LS LS 21/36 42/72 200 100 253 # 198 # 7 8.8 4 4 19.2/1.7 25.4/0.8
Tranchart et al. [45] 28 28 LS, PS LS, PS 0/28 0/28 200 150 210 # 176 # 14 7.1 6 5.5 17.8/10.7 17.8/10.7
Berber et al. [46] 9 23 LLS LLS 0/9 0/12 136* 155* 258* 234* 1 0 - - 11/- 17/-
Yu et al. [47] 13 17 LS LS 3/10 11/6 388 343 291 241 0 0 7.8* 9.5* 0 11.7/-
Zeng et al. [48] 3 5 LS LS 0/3 0/5 316* 290* 370* 249* 0 20 3 5 - -
Lin et al. [49] 25 11 LS LS 3/25 2/11 271 295 319 315 - - 7.5 7 24/- 27.2/-
In case of PSM, only its data were reported. R: robotic surgery; L: laparoscopic surgery. °: referred to the sub-group of HCC. Cases:
number of patients. Lesions location: PS:postero-superior segments; LS: laparoscopic segments different from the postero-superiors;
LLS: left-lateral sectionectomy. Major/minor resections: number of major/minor, according to the description of the authors or calculated
from the data supplied. EBL: milliliters (median/*mean). Operative time: minutes (median/*mean). Conversion rate: percentage of
procedures converted to open surgery. LoS: days (median/*mean). Overall/major complications: percentage of all complications/major
#
complications. Statistically significant results (P-value < 0.05) are expressed “ ”, if reported in the articles. “-”: not reported
Robotic vs. laparoscopic liver surgery
Twenty-five comparative studies between robotic and laparoscopic liver surgery, including 1,043 cases (range
3-115) and 1,385 cases (range 5-223) respectively, were reviewed [Table 2]. These reports were published
from 2010 to 2020. All of them were retrospective and 5 were propensity score matching studies (PSM). In
case of PSM only results of the matchings were considered.
Left lateral sectionectomy
Left lateral sectionectomy (LLS) is currently performed with laparoscopy as a standard of care. Five
studies focused on robotic and laparoscopic LLS, including 106 (range 9-58) and 206 (range 18-80) cases,
respectively. Most of the articles reported similar perioperative outcomes between laparoscopy and RS.
Many authors concluded that laparoscopic LLS remains the gold standard, since RS did not add any
[13]
significant benefit, but increased the costs [13,37-39] . However, Hu et al. established that RS could be the
best choice to treat complex cases of LLS (tumor size > 10 cm in diameter, proximity of the tumor to
major vessels, BMI > 30 kg/m , combined lymphadenectomy or choledochoscopy, huge left lateral section
2
embedded in splenic fossa), reporting significantly lower EBL than in laparoscopy for these cases (131.9 mL
vs. 320.8 mL, respectively).