Page 68 - Read Online
P. 68
Page 4 of 15 Ruzzenente et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:91 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.90
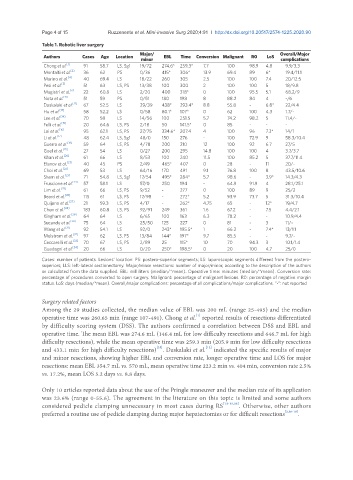
Table 1. Robotic liver surgery
Authors Cases Age Location Major/ EBL Time Conversion Malignant R0 LoS Overall/Major
minor complications
Chong et al. [1] 91 58.7 LS, Sg1 19/72 274.6* 259.3* 7.7 100 98.9 4.8 9.9/3.3
Montalti et al. [2] 36 62 PS 0/36 415* 306* 13.9 69.4 89 6* 19.4/11.1
Marino et al. [4] 40 69.4 LS 18/22 260 305 2.5 100 100 7.4 20/12.5
Pesi et al. [5] 51 63 LS, PS 13/38 100 300 2 100 100 5 18/9.8
Magistri et al. [6] 22 60.8 LS 2/20 400 318* 0 100 95.5 5.1 68.2/9
Nota et al. [11] 51 59 PS 0/51 180 198 8 88.2 84 4 -/6
Daskalaki et al. [12] 67 52.5 LS 29/39 438* 293.4* 8.8 55.8 - 6.8* 22/4.4
Hu et al. [13] 58 52.2 LS 0/58 80.1* 107* 0 62 100 4.3 1.7/-
Lee et al. [14] 70 58 LS 14/56 100 251.5 5.7 74.2 98.2 5 11.4/-
Felli et al. [15] 20 64.6 LS, PS 2/18 50 141.5* 0 85 - - -
Lai et al. [16] 95 62.1 LS, PS 27/75 334.6* 207.4 4 100 96 7.3* 14/1
Li et al. [17] 48 62.4 LS, Sg1 48/0 150 276 - 100 72.9 9 58.3/10.4
Guerra et al. [18] 59 64 LS, PS 4/78 200 210 12 100 92 6.7 27/5
Goel et al. [19] 27 54 LS 0/27 200 295 14.8 100 100 4 3.7/3.7
Khan et al. [20] 61 66 LS 8/53 100 240 11.5 100 85.2 5 37.7/11.4
Efanov et al. [21] 40 45 PS 2/49 465* 407 0 28 - 11 20/-
Choi et al. [22] 69 53 LS 64/16 170 491 9.1 76.8 100 8 43.5/10.6
Sham et al. [23] 71 54.8 LS, Sg1 17/54 495* 284* 5.7 98.6 - 3.9* 14.3/4.3
Fruscione et al. [24] 57 58.1 LS 57/0 250 194 - 64.9 91.9 4 28.1/25.1
Lim et al. [25] 61 66 LS, PS 9/52 - 277 0 100 89 9 25/2
Beard et al. [26] 115 61 LS, PS 17/98 - 272* 5.2 93.9 73.7 5 31.3/10.4
Quijano et al. [27] 21 59.3 LS, PS 4/17 - 262* 4.75 65 - 12* 19/4.7
Chen et al. [28] 183 60.8 LS, PS 92/91 249 361 1.6 67.2 - 7.5 4.4/2.1
Kingham et al. [29] 64 64 LS 6/65 100 163 6.3 78.2 - - 10.9/4.4
Sucandy et al. [30] 75 64 LS 25/50 125 227 0 81 - 3 11/-
Wang et al. [31] 92 54.1 LS 92/0 243* 195.5* 1 66.3 - 7.4* 13/1.1
Melstrom et al. [32] 97 62 LS, PS 13/84 144* 197* 9.7 85.5 - - 9.7/-
Ceccarelli et al. [33] 70 67 LS, PS 2/89 25 115* 10 70 94.3 3 10.1/1.4
Guadagni et al. [34] 20 66 LS 0/20 250* 198.5* 0 20 100 4.7 25/0
Cases: number of patients. Lesions’ location: PS: postero-superior segments; LS: laparoscopic segments different from the postero-
superiors; LLS: left-lateral sectionectomy. Major/minor resections: number of major/minor, according to the description of the authors
or calculated from the data supplied. EBL: milliliters (median/*mean). Operative time: minutes (median/*mean). Conversion rate:
percentage of procedures converted to open surgery. Malignant: percentage of malignant lesions. R0: percentage of negative margin
status. LoS: days (median/*mean). Overall/major complications: percentage of all complications/major complications. “-”: not reported
Surgery related factors
Among the 29 studies collected, the median value of EBL was 200 mL (range 25-495) and the median
[1]
operative time was 260.65 min (range 107-491). Chong et al. reported results of resections differentiated
by difficulty scoring system (DSS). The authors confirmed a correlation between DSS and EBL and
operative time. The mean EBL was 274.6 mL (146.4 mL for low difficulty resections and 646.7 mL for high
difficulty resections), while the mean operative time was 259.3 min (205.9 min for low difficulty resections
[12]
[35]
and 433.1 min for high difficulty resections) . Daskalaki et al. indicated the specific results of major
and minor resections, showing higher EBL and conversion rate, longer operative time and LOS for major
resections: mean EBL 354.7 mL vs. 570 mL, mean operative time 223.2 min vs. 404 min, conversion rate 2.5%
vs. 17.2%, mean LOS 5.2 days vs. 8.8 days.
Only 10 articles reported data about the use of the Pringle maneuver and the median rate of its application
was 23.6% (range 0-55.6). The agreement in the literature on this topic is limited and some authors
considered pedicle clamping unnecessary in most cases during RS [13-15,36] . Otherwise, other authors
preferred a routine use of pedicle clamping during major hepatectomies or for difficult resections [2,16-18] .