Page 71 - Read Online
P. 71
Fontan et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:29 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.09 Page 5 of 11
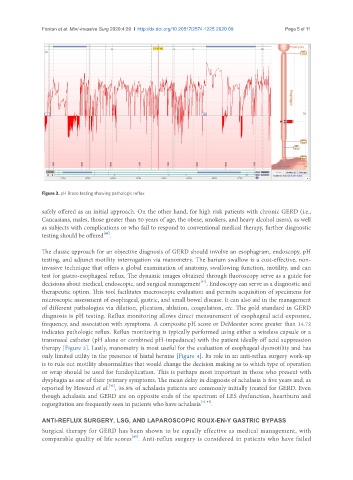
Figure 3. pH Bravo testing showing pathologic reflux
safely offered as an initial approach. On the other hand, for high risk patients with chronic GERD (i.e.,
Caucasians, males, those greater than 50 years of age, the obese, smokers, and heavy alcohol users), as well
as subjects with complications or who fail to respond to conventional medical therapy, further diagnostic
[40]
testing should be offered .
The classic approach for an objective diagnosis of GERD should involve an esophagram, endoscopy, pH
testing, and adjunct motility interrogation via manometry. The barium swallow is a cost-effective, non-
invasive technique that offers a global examination of anatomy, swallowing function, motility, and can
test for gastro-esophageal reflux. The dynamic images obtained through fluoroscopy serve as a guide for
[41]
decisions about medical, endoscopic, and surgical management . Endoscopy can serve as a diagnostic and
therapeutic option. This tool facilitates macroscopic evaluation and permits acquisition of specimens for
microscopic assessment of esophageal, gastric, and small bowel disease. It can also aid in the management
of different pathologies via dilation, plication, ablation, coagulation, etc. The gold standard in GERD
diagnosis is pH testing. Reflux monitoring allows direct measurement of esophageal acid exposure,
frequency, and association with symptoms. A composite pH score or DeMeester score greater than 14.72
indicates pathologic reflux. Reflux monitoring is typically performed using either a wireless capsule or a
transnasal catheter (pH alone or combined pH-impedance) with the patient ideally off acid suppression
therapy [Figure 3]. Lastly, manometry is most useful for the evaluation of esophageal dysmotility and has
only limited utility in the presence of hiatal hernias [Figure 4]. Its role in an anti-reflux surgery work-up
is to rule out motility abnormalities that would change the decision making as to which type of operation
or wrap should be used for fundoplication. This is perhaps most important in those who present with
dysphagia as one of their primary symptoms. The mean delay in diagnosis of achalasia is five years and, as
[42]
reported by Howard et al. , 36.8% of achalasia patients are commonly initially treated for GERD. Even
though achalasia and GERD are on opposite ends of the spectrum of LES dysfunction, heartburn and
regurgitation are frequently seen in patients who have achalasia [42-44] .
ANTI-REFLUX SURGERY, LSG, AND LAPAROSCOPIC ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
Surgical therapy for GERD has been shown to be equally effective as medical management, with
[45]
comparable quality of life scores . Anti-reflux surgery is considered in patients who have failed