Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Moroni et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2019;3:36 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.34 Page 7 of 12
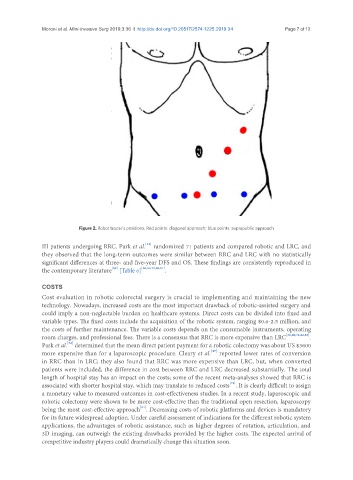
Figure 2. Robot trocar's positions. Red points: diagonal approach; blue points: suprapublic approach
[31]
III patients undergoing RRC. Park et al. randomized 71 patients and compared robotic and LRC, and
they observed that the long-term outcomes were similar between RRC and LRC with no statistically
significant differences at three- and five-year DFS and OS. These findings are consistently reproduced in
[80]
the contemporary literature [Table 6] [20,30,72,80,81] .
COSTS
Cost evaluation in robotic colorectal surgery is crucial to implementing and maintaining the new
technology. Nowadays, increased costs are the most important drawback of robotic-assisted surgery and
could imply a non-neglectable burden on healthcare systems. Direct costs can be divided into fixed and
variable types. The fixed costs include the acquisition of the robotic system, ranging $0.6-2.5 million, and
the costs of further maintenance. The variable costs depends on the consumable instruments, operating
room charges, and professional fees. There is a consensus that RRC is more expensive than LRC [36,60,74,82,83] .
[72]
Park et al. determined that the mean direct patient payment for a robotic colectomy was about US $3600
[27]
more expensive than for a laparoscopic procedure. Cleary et al. reported lower rates of conversion
in RRC than in LRC; they also found that RRC was more expensive than LRC, but, when converted
patients were included, the difference in cost between RRC and LRC decreased substantially. The total
length of hospital stay has an impact on the costs; some of the recent meta-analyses showed that RRC is
[73]
associated with shorter hospital stay, which may translate to reduced costs . It is clearly difficult to assign
a monetary value to measured outcomes in cost-effectiveness studies. In a recent study, laparoscopic and
robotic colectomy were shown to be more cost-effective than the traditional open resection, laparoscopy
[84]
being the most cost-effective approach . Decreasing costs of robotic platforms and devices is mandatory
for its future widespread adoption. Under careful assessment of indications for the different robotic system
applications, the advantages of robotic assistance, such as higher degrees of rotation, articulation, and
3D imaging, can outweigh the existing drawbacks provided by the higher costs. The expected arrival of
competitive industry players could dramatically change this situation soon.