Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Page 8 of 10 Cortes-Cerisuelo et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2019;3:1 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.60
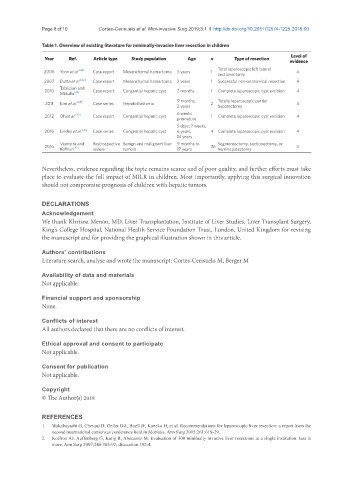
Table 1. Overview of existing literature for minimally-invasive liver resection in children
Level of
Year Ref. Article type Study population Age n Type of resection
evidence
Total laparoscopic left lateral
2006 Yoon et al. [44] Case report Mesenchymal hamartoma 5 years 1 4
sectionectomy
2007 Dutta et al. [42] Case report Mesenchymal hamartoma 2 years 1 Successful non-anatomical resection 4
Tabrizian and
2010 [34] Case report Congential hepatic cyst 2 months 1 Complete laparoscopic cyst excision 4
Midulla
9 months, Totally laparoscopic partial
[45]
2011 Kim et al. Case series Hepatoblastoma 2 4
2 years hepatectomy
6 weeks
[43]
2012 Oh et al. Case report Congential hepatic cyst 1 Complete laparoscopic cyst excision 4
premature
5 days, 7 weeks,
2016 Linden et al. [35] Case series Congential hepatic cyst 6 years, 4 Complete laparoscopic cyst excision 4
14 years
Veenstra and Restrospective Benign and malignant liver 9 months to Segmentectomy, sectionectomy, or
2016 [47] 36 3
Koffron review tumors 17 years hemihepatectomy
Nevertheless, evidence regarding the topic remains scarce and of poor quality, and further efforts must take
place to evaluate the full impact of MILR in children. Most importantly, applying this surgical innovation
should not compromise prognosis of children with hepatic tumors.
DECLARATIONS
Acknowledgement
We thank Khrisna Menon, MD, Liver Transplantation, Institute of Liver Studies, Liver Transplant Surgery,
King’s College Hospital, National Health Service Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom for revising
the manuscript and for providing the graphical illustration shown in this article.
Authors’ contributions
Literature search, analyse and wrote the manuscript: Cortes-Cerisuelo M, Berger M
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Copyright
© The Author(s) 2019.
REFERENCES
1. Wakabayashi G, Cherqui D, Geller DA, Buell JF, Kaneko H, et al. Recommendations for laparoscopic liver resection: a report from the
second international consensus conference held in Morioka. Ann Surg 2015;261:619-29.
2. Koffron AJ, Auffenberg G, Kung R, Abecassis M. Evaluation of 300 minimally invasive liver resections at a single institution: less is
more. Ann Surg 2007;246:385-92; discussion 392-4.