Page 184 - Read Online
P. 184
Chen et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2018;2:42 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.59 Page 11 of 17
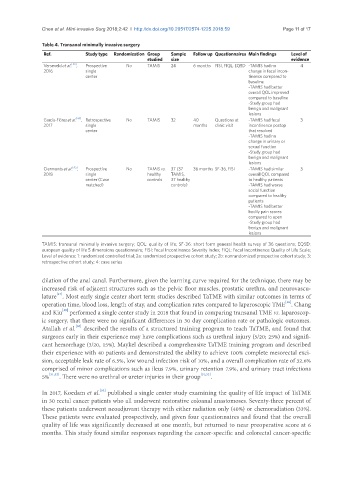
Table 4. Transanal minimally invasive surgery
Ref. Study type Randomization Group Sample Follow up Questionnaires Main findings Level of
studied size evidence
Verseveld et al. [43] , Prospective No TAMIS 24 6 months FISI, FIQL, EQ5D -TAMIS had no 4
2016 single change in fecal incon-
center tinence compared to
baseline
-TAMIS had better
overall QOL improved
compared to baseline
-Study group had
benign and malignant
lesions
García-Flórez et al. [44] , Retrospective No TAMIS 32 40 Questions at -TAMIS had fecal 3
2017 single months clinic visit incontinence postop
center that resolved
-TAMIS had no
change in urinary or
sexual function
-Study group had
benign and malignant
lesions
Clermonts et al. [45] , Prospective No TAMIS vs. 37 (37 36 months SF-36, FISI -TAMIS had similar 3
2018 single healthy TAMIS, overall QOL compared
center (Case controls 37 healthy to healthy patients
matched) controls) -TAMIS had worse
social function
compared to healthy
patients
-TAMIS had better
bodily pain scores
compared to open
-Study group had
benign and malignant
lesions
TAMIS: transanal minimally invasive surgery; QOL: quality of life; SF-36: short form general health survey of 36 questions; EQ5D:
european quality of life 5 dimensions questionnaire; FISI: Fecal Incontinence Severity Index; FIQL: Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life Scale;
Level of evidence: 1: randomized controlled trial; 2a: randomized prospective cohort study; 2b: nonrandomized prospective cohort study; 3:
retrospective cohort study; 4: case series
dilation of the anal canal. Furthermore, given the learning curve required for the technique, there may be
increased risk of adjacent structures such as the pelvic floor muscles, prostatic urethra, and neurovascu-
lature . Most early single center short term studies described TaTME with similar outcomes in terms of
[47]
[48]
operation time, blood loss, length of stay, and complication rates compared to laparoscopic TME . Chang
[49]
and Kiu performed a single center study in 2018 that found in comparing transanal TME vs. laparoscop-
ic surgery, that there were no significant differences in 30 day complication rate or pathologic outcomes.
[50]
Atallah et al. described the results of a structured training program to teach TaTME, and found that
surgeons early in their experience may have complications such as urethral injury (5/20; 25%) and signifi-
cant hemorrhage (3/20, 15%). Maykel described a comprehensive TaTME training program and described
their experience with 40 patients and demonstrated the ability to achieve 100% complete mesorectal exci-
sion, acceptable leak rate of 6.5%, low wound infection risk of 10%, and a overall complication rate of 32.6%
comprised of minor complications such as ileus 7.9%, urinary retention 7.9%, and urinary tract infections
5% [51,52] . There were no urethral or ureter injuries in their group [51,52] .
In 2017, Koedam et al. published a single center study examining the quality of life impact of TaTME
[53]
in 30 rectal cancer patients who all underwent restorative coloanal anastomoses. Seventy-three percent of
these patients underwent neoadjuvant therapy with either radiation only (40%) or chemoradiation (33%).
These patients were evaluated prospectively, and given four questionnaires and found that the overall
quality of life was significantly decreased at one month, but returned to near preoperative score at 6
months. This study found similar responses regarding the cancer-specific and colorectal cancer-specific