Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Page 127 Fanella et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:124-9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.11
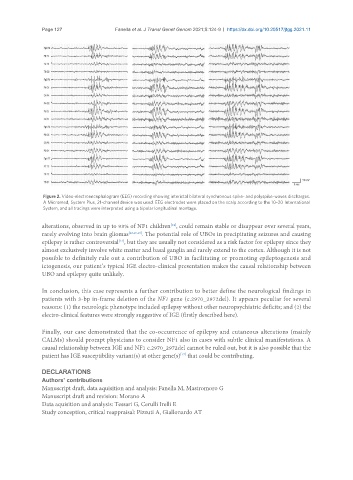
Figure 2. Video-electroencephalogram (EEG) recording showing interictal bilateral synchronous spike- and polyspike-waves discharges.
A Micromed, System Plus, 21-channel device was used. EEG electrodes were placed on the scalp according to the 10-20 International
System, and all tracings were interpreted using a bipolar longitudinal montage.
[14]
alterations, observed in up to 93% of NF1 children , could remain stable or disappear over several years,
rarely evolving into brain gliomas [12,15,16] . The potential role of UBOs in precipitating seizures and causing
[12]
epilepsy is rather controversial , but they are usually not considered as a risk factor for epilepsy since they
almost exclusively involve white matter and basal ganglia and rarely extend to the cortex. Although it is not
possible to definitely rule out a contribution of UBO in facilitating or promoting epileptogenesis and
ictogenesis, our patient’s typical IGE electro-clinical presentation makes the causal relationship between
UBO and epilepsy quite unlikely.
In conclusion, this case represents a further contribution to better define the neurological findings in
patients with 3-bp in-frame deletion of the NF1 gene (c.2970_2972del). It appears peculiar for several
reasons: (1) the neurologic phenotype included epilepsy without other neuropsychiatric deficits; and (2) the
electro-clinical features were strongly suggestive of IGE (firstly described here).
Finally, our case demonstrated that the co-occurrence of epilepsy and cutaneous alterations (mainly
CALMs) should prompt physicians to consider NF1 also in cases with subtle clinical manifestations. A
causal relationship between IGE and NF1 c.2970_2972del cannot be ruled out, but it is also possible that the
patient has IGE susceptibility variant(s) at other gene(s) that could be contributing.
[17]
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Manuscript draft, data aquisition and analysis: Fanella M, Mastromoro G
Manuscript draft and revision: Morano A
Data aquisition and analysis: Tessari G, Cerulli Irelli E
Study conception, critical reappraisal: Pizzuti A, Giallonardo AT