Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Page 272 Arroyo Seguí et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:263-77 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.35
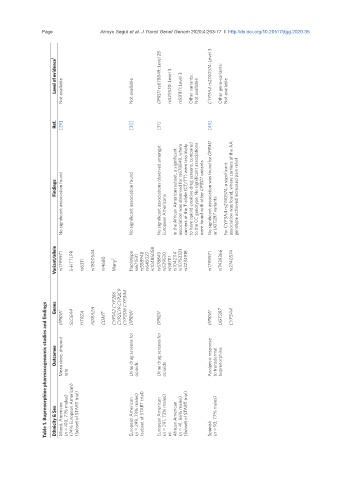
Level of evidence 1 Not available Not available OPRD1 rs678849: Level 2B rs529520: Level 3 rs581111: Level 3 Other variants: Not available CYP3A4 rs2740574: Level 3 Other gene-variants: Not available
Ref. [29] [30] [31] [45]
No significant association found No significant association found European Americans were found with other OPRD1 variants or UGT2B7 variants For CYP3A4 rs2740574, a significant genotype achieved increased pain relief
Findings No significant associations observed amongst In the African American subset, a significant association was observed for rs678849, where carriers of the T-allele (CT/TT) were less likely to have opioid-positive drug screens, compared to the CC genotype. No significant associations No significant association was found for OPRM1 association was found, where carriers of the AA
Variant/allele rs1799971 5-HTTLPR rs6311 rs1800544 rs4680 Many 2 Haplotype: rs671531 rs558948 rs645027 rs10485058 rs678849 rs529520 rs581111 rs1042114 rs10753331 rs2234918 rs1799971 rs7439366 rs2740574
Genes CYP1A2 CYP2B6 CYP2C19 CYP2C9 CYP2D6 CYP3A4
Table 1. Buprenorphine pharmacogenomic studies and findings
OPRM1 SLC6A4 HTR2A ADRA2A COMT OPRM1 OPRD1 OPRM1 UGT2B7 CYP3A4
Outcomes Mean dose, dropout rate Urine drug screens for opioids Urine drug screens for opioids Analgesic response to transdermal buprenorphine
Ethnicity & Sex Mixed, American (n = 410, 71% males) (74% European American) (Subset of START trial) European American (n = 299, 73% males) (subset of START trial) European American (n = 291, 73% males) vs. African American (n = 41, 66% males) (Subset of START trial) Spanish (n = 93, 77% males)