Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Khajuria et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:91-103 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.06 Page 97
A
B
C
D
E
F
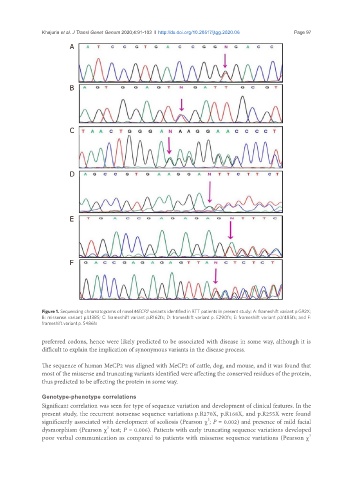
Figure 1. Sequencing chromatograms of novel MECP2 variants identified in RTT patients in present study: A: frameshift variant p.G92X;
B: missense variant p.L138S; C: frameshift variant p.R162fs; D: frameshift variant p. E290fs; E: frameshift variant p.V485fs; and F:
frameshift variant p. S486fs
preferred codons, hence were likely predicted to be associated with disease in some way, although it is
difficult to explain the implication of synonymous variants in the disease process.
The sequence of human MeCP2 was aligned with MeCP2 of cattle, dog, and mouse, and it was found that
most of the missense and truncating variants identified were affecting the conserved residues of the protein,
thus predicted to be affecting the protein in some way.
Genotype-phenotype correlations
Significant correlation was seen for type of sequence variation and development of clinical features. In the
present study, the recurrent nonsense sequence variations p.R270X, p.R168X, and p.R255X were found
2
significantly associated with development of scoliosis (Pearson χ ; P = 0.002) and presence of mild facial
2
dysmorphism (Pearson χ test; P = 0.006). Patients with early truncating sequence variations developed
2
poor verbal communication as compared to patients with missense sequence variations (Pearson χ