Page 38 - Read Online
P. 38
Page 96 Khajuria et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:91-103 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.06
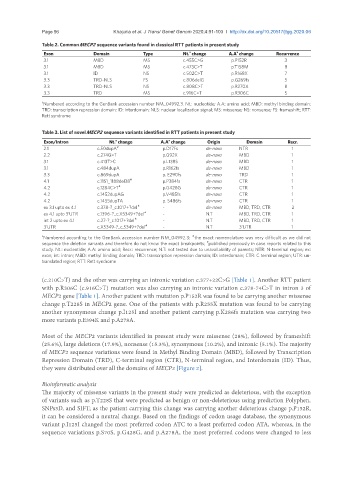
Table 2. Common MECP2 sequence variants found in classical RTT patients in present study
Exon Domain Type Nt. change A.A change Recurrence
a
a
3.1 MBD MS c.455C>G p.P152R 3
3.1 MBD MS c.473C>T p.T158M 8
3.1 ID NS c.502C>T p.R168X 7
3.3 TRD-NLS FS c.806delG p.G269fs 5
3.3 TRD-NLS NS c.808C>T p.R270X 8
3.3 TRD MS c.916C>T p.R306C 5
a Numbered according to the GenBank accession number NM_04992.3. Nt.: nucleotide; A.A: amino acid; MBD: methyl binding domain;
TRD: transcription repression domain; ID: interdomain; NLS: nuclear localization signal; MS: missense; NS: nonsense; FS: frameshift; RTT:
Rett syndrome
Table 3. List of novel MECP2 sequence variants identified in RTT patients in present study
a
a
Exon/Intron Nt. change A.A change Origin Domain Recr.
2.1 c.50dupA # p.D17Fs de-novo NTR 1
2.2 c.274G>T p.G92X de-novo MBD 1
3.1 c.413T>C p.L138S de-novo MBD 1
3.1 c.484dupA p.R162fs de-novo MBD 1
3.3 c.869dupA p. E290fs de-novo TRD 1
4.1 c.1151_1188del38 # p.P384fs de-novo CTR 1
4.2 c.1284C>T # p.G428G de-novo CTR 1
4.2 c.1452dupAG p.V485fs de-novo CTR 1
4.2 c.1455dupTA p. S486fs de-novo CTR 1
ex 3.1 upto ex 4.1 c.378-?_c.1017+?del « - de-novo MBD, TRD, CTR 2
ex 4.1 upto 3’UTR c.1396-?_c.X5349+?del « - N.T MBD, TRD, CTR 1
int 2 upto ex 4.1 c.27-?_c.1017+?del « - N.T MBD, TRD, CTR 1
3’UTR c.X5349-?_c.5349+?del « - N.T 3’UTR 1
a Numbered according to the GenBank accession number NM_04992.3; the exact nomenclature was very difficult as we did not
«
#
sequence the deletion variants and therefore do not know the exact breakpoints; published previously in case reports related to this
study. Nt.: nucleotide; A.A: amino acid; Recr.: recurrence; N.T: not tested due to unavailability of parents; NTR: N-terminal region; ex:
exon; int: intron; MBD: methyl binding domain; TRD: transcription repression domain; ID: interdomain; CTR: C terminal region; UTR: un-
translated region; RTT: Rett syndrome
(c.210C>T) and the other was carrying an intronic variation c.377+22C>G [Table 1]. Another RTT patient
with p.R306C (c.916C>T) mutation was also carrying an intronic variation c.378-74C>T in intron 3 of
MECP2 gene [Table 1]. Another patient with mutation p.P152R was found to be carrying another missense
change p.T228S in MECP2 gene. One of the patients with p.R255X mutation was found to be carrying
another synonymous change p.I125I and another patient carrying p.K286fs mutation was carrying two
more variants p.E394K and p.A278A.
Most of the MECP2 variants identified in present study were missense (28%), followed by frameshift
(25.6%), large deletions (17.9%), nonsense (15.3%), synonymous (10.2%), and intronic (5.1%). The majority
of MECP2 sequence variations were found in Methyl Binding Domain (MBD), followed by Transcription
Repression Domain (TRD), C-terminal region (CTR), N-terminal region, and Interdomain (ID). Thus,
they were distributed over all the domains of MECP2 [Figure 2].
Bioinformatic analysis
The majority of missense variants in the present study were predicted as deleterious, with the exception
of variants such as p.T228S that were predicted as benign or non-deleterious using prediction Polyphen,
SNPs3D, and SIFT; as the patient carrying this change was carrying another deleterious change p.P152R,
it can be considered a neutral change. Based on the findings of codon usage database, the synonymous
variant p.I125I changed the most preferred codon ATC to a least preferred codon ATA, whereas, in the
sequence variations p.S70S, p.G428G, and p.A278A, the most preferred codons were changed to less