Page 14 - Read Online
P. 14
Page 52 Franz et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:50-70 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.13
Figure 1. Number of articles featuring tRNA-related issues in the context of impaired human cognition between 1994 and the present
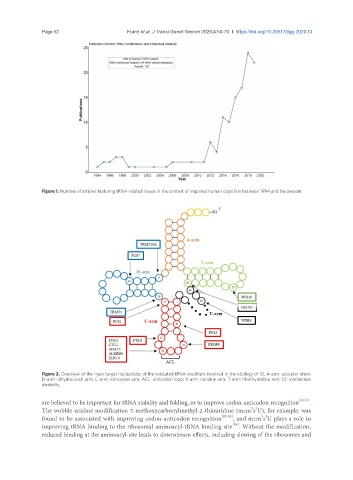
Figure 2. Overview of the main target nucleotides of the indicated tRNA modifiers involved in the etiology of ID. A-arm: acceptor stem;
D-arm: dihydrouracil arm; C-arm: anticodon arm; ACL: anticodon loop; V-arm: variable arm; T-arm: ribothymidine arm; ID: intellectual
disability
are believed to be important for tRNA stability and folding, or to improve codon-anticodon recognition [19-21] .
5 2
The wobble-uridine modification 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine (mcm s U), for example, was
5 2
found to be associated with improving codon-anticodon recognition [22-25] , and mcm s U plays a role in
[26]
improving tRNA binding to the ribosomal aminoacyl-tRNA binding site . Without the modification,
reduced binding at the aminoacyl-site leads to downstream effects, including slowing of the ribosomes and