Page 117 - Read Online
P. 117
Page 254 Dana et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:251-62 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.25
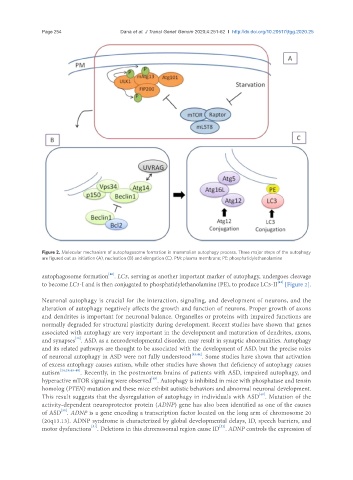
Figure 2. Molecular mechanism of autophagosome formation in mammalian autophagy process. Three major steps of the autophagy
are figured out as initiation (A), nucleation (B) and elongation (C). PM: plasma membrane; PE: phosphatidylethanolamine
[40]
autophagosome formation . LC3, serving as another important marker of autophagy, undergoes cleavage
[41]
to become LC3-I and is then conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), to produce LC3-II [Figure 2].
Neuronal autophagy is crucial for the interaction, signaling, and development of neurons, and the
alteration of autophagy negatively affects the growth and function of neurons. Proper growth of axons
and dendrites is important for neuronal balance. Organelles or proteins with impaired functions are
normally degraded for structural plasticity during development. Recent studies have shown that genes
associated with autophagy are very important in the development and maturation of dendrites, axons,
[42]
and synapses . ASD, as a neurodevelopmental disorder, may result in synaptic abnormalities. Autophagy
and its related pathways are thought to be associated with the development of ASD, but the precise roles
of neuronal autophagy in ASD were not fully understood [43,44] . Some studies have shown that activation
of excess autophagy causes autism, while other studies have shown that deficiency of autophagy causes
autism [24,29,45-48] . Recently, in the postmortem brains of patients with ASD, impaired autophagy, and
[45]
hyperactive mTOR signaling were observed . Autophagy is inhibited in mice with phosphatase and tensin
homolog (PTEN) mutation and these mice exhibit autistic behaviors and abnormal neuronal development.
[49]
This result suggests that the dysregulation of autophagy in individuals with ASD . Mutation of the
activity-dependent neuroprotector protein (ADNP) gene has also been identified as one of the causes
[50]
of ASD . ADNP is a gene encoding a transcription factor located on the long arm of chromosome 20
(20q13.13). ADNP syndrome is characterized by global developmental delays, ID, speech barriers, and
[52]
[51]
motor dysfunctions . Deletions in this chromosomal region cause ID . ADNP controls the expression of