Page 98 - Read Online
P. 98
Page 6 of 20 Rhoades et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2019;3:1. I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2018.26
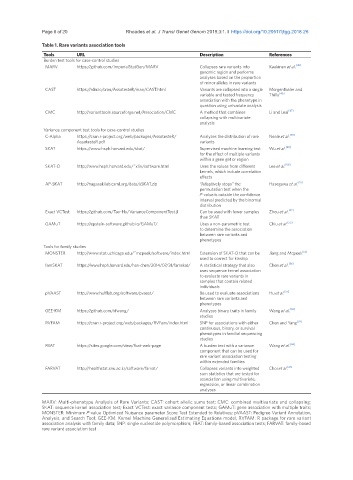
Table 1. Rare variants association tools
Tools URL Description References
Burden test tools for case-control studies
MARV https://github.com/ImperialStatGen/MARV Collapses rare variants into Kaakinen et al. [45]
genomic region and performs
analyses based on the proportion
of minor alleles in rare variants
CAST https://rdrr.io/cran/AssotesteR/man/CAST.html Variants are collapsed into a single Morgenthaler and
variable and tested frequency Thilly [46]
association with the phenotype in
question using univariate analysis
CMC http://varianttools.sourceforge.net/Association/CMC A method that combines Li and Leal [47]
collapsing with multivariate
analysis
Variance component test tools for case-control studies
C-Alpha https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/AssotesteR/ Analyzes the distribution of rare Neale et al. [48]
AssotesteR.pdf variants
SKAT https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/skat/ Supervised machine learning test Wu et al. [49]
for the effect of multiple variants
within a gene get or region
SKAT-O http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/˜xlin/software.html Uses the values from different Lee et al. [50]
kernels, which include correlation
effects
AP-SKAT http://nagasakilab.csml.org/data/aSKAT.zip “Adaptively stops” the Hasegawa et al. [51]
permutation test when the
P-value is outside the confidence
interval predicted by the binomial
distribution
Exact VCTest https://github.com/Tao-Hu/VarianceComponentTest.jl Can be used with fewer samples Zhou et al. [52]
than SKAT
GAMuT https://epstein-software.github.io/GAMuT/ Uses a non-parametric test Chiu et al. [53]
to determine the association
between rare variants and
phenotypes
Tools for family studies
MONSTER http://www.stat.uchicago.edu/˜mcpeek/software/index.html Extension of SKAT-O that can be Jiang and Mcpeek [55]
used to correct for kinship
famSKAT https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/han-chen/2014/07/31/famskat/ A statistical strategy that also Chen et al. [56]
uses sequence kernel association
to evaluate rare variants in
samples that contain related
individuals
pVAAST http://www.hufflab.org/software/pvaast/ Be used to evaluate associations Hu et al. [57]
between rare variants and
phenotypes
GEE-KM https://github.com/xfwang/ Analyzes binary traits in family Wang et al. [58]
studies
RVFAM https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/RVFam/index.html SNP for associations with either Chen and Yang [59]
continuous, binary, or survival
phenotypes in familial sequencing
studies
FBAT https://sites.google.com/view/fbat-web-page A burden test with a variance Wang et al. [60]
component that can be used for
rare variant association testing
within extended families
FARVAT http://healthstat.snu.ac.kr/software/farvat/ Collapses variants into weighted Choi et al. [61]
sum statistics that are tested for
association using multivariate,
regression, or linear combination
analyses
MARV: Multi-phenotype Analysis of Rare Variants; CAST: cohort allelic sums test; CMC: combined multivariate and collapsing;
SKAT: sequence kernel association test; Exact VCTest: exact variance component tests; GAMuT: gene association with multiple traits;
MONSTER: Minimum P-value Optimized Nuisance parameter Score Test Extended to Relatives; pVAAST: Pedigree Variant Annotation,
Analysis, and Search Tool; GEE-KM: Kernel Machine Generalized Estimating Equations model; RVFAM: R package for rare variant
association analysis with family data; SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism; FBAT: family-based association tests; FARVAT: family-based
rare variant association test