Page 54 - Read Online
P. 54
Page 8 of 10 Barwell et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2018;2:13. I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2018.17
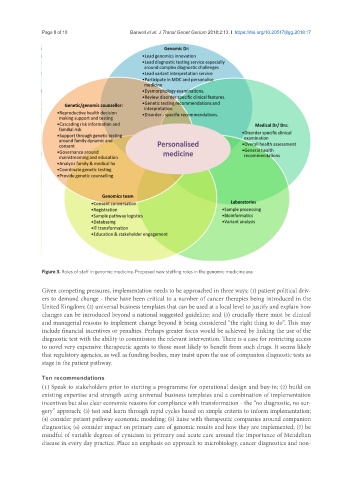
Figure 3. Roles of staff in genomic medicine. Proposed new staffing roles in the genomic medicine era
Given competing pressures, implementation needs to be approached in three ways: (1) patient political driv-
ers to demand change - these have been critical to a number of cancer therapies being introduced in the
United Kingdom; (2) universal business templates that can be used at a local level to justify and explain how
changes can be introduced beyond a national suggested guideline; and (3) crucially there must be clinical
and managerial reasons to implement change beyond it being considered “the right thing to do”. This may
include financial incentives or penalties. Perhaps greater focus would be achieved by linking the use of the
diagnostic test with the ability to commission the relevant intervention. There is a case for restricting access
to novel very expensive therapeutic agents to those most likely to benefit from such drugs. It seems likely
that regulatory agencies, as well as funding bodies, may insist upon the use of companion diagnostic tests as
stage in the patient pathway.
Ten recommendations
(1) Speak to stakeholders prior to starting a programme for operational design and buy-in; (2) build on
existing expertise and strength using universal business templates and a combination of implementation
incentives but also clear economic reasons for compliance with transformation - the “no diagnostic, no sur-
gery” approach; (3) test and learn through rapid cycles based on simple criteria to inform implementation;
(4) consider patient pathway economic modeling; (5) liaise with therapeutic companies around companion
diagnostics; (6) consider impact on primary care of genomic results and how they are implemented; (7) be
mindful of variable degrees of cynicism in primary and acute care around the importance of Mendelian
disease in every day practice. Place an emphasis on approach to microbiology, cancer diagnostics and non-